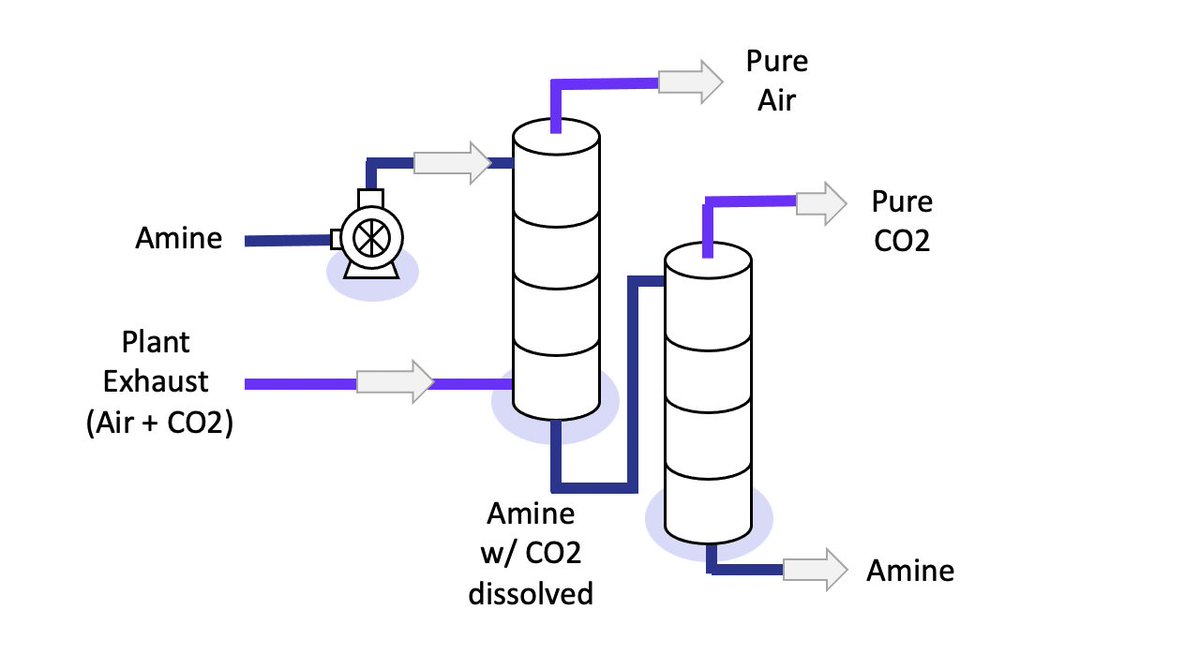
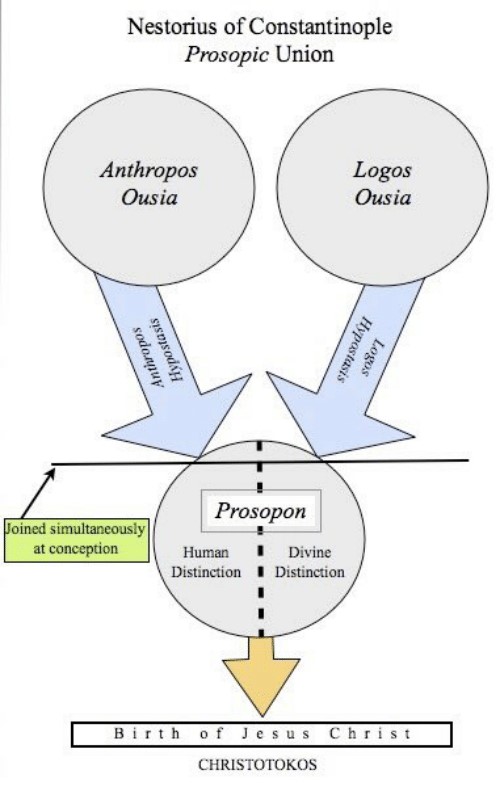
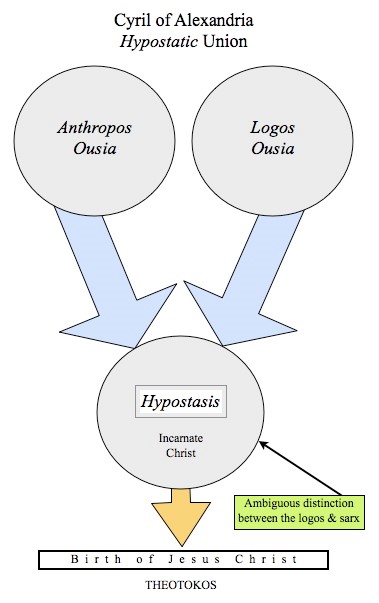
More from NotTheMacAnon
👍🏻
https://t.co/0ywQ1y5NDj
Pott found an association between exposure to soot and a high incidence of scrotal skin cancer in chimney sweeps. This cancer is now known as Pott's or chimney sweep cancer.
Coal contains trace amounts of naturally-occurring radioactive elements. The process of burning coal at coal-fired power plants, called combustion, creates wastes that contain small amounts of naturally-occurring radioactive material (NORM).
Fly ash particles (a major component of coal ash) can become lodged in the deepest part of your lungs, where they trigger asthma, inflammation and immunological reactions.
"When does a canary sing"
— Found&Forgiven (@AshlieMC2) December 7, 2020
See thread RT on oxidative stress and QD effects.
Thank you @NotTheMacAnon1https://t.co/XlyXyiCS2H
https://t.co/0ywQ1y5NDj
Pott found an association between exposure to soot and a high incidence of scrotal skin cancer in chimney sweeps. This cancer is now known as Pott's or chimney sweep cancer.
Coal contains trace amounts of naturally-occurring radioactive elements. The process of burning coal at coal-fired power plants, called combustion, creates wastes that contain small amounts of naturally-occurring radioactive material (NORM).
Fly ash particles (a major component of coal ash) can become lodged in the deepest part of your lungs, where they trigger asthma, inflammation and immunological reactions.
Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
https://t.co/mzS7vVSREJ
https://t.co/353PdAX2fa
https://t.co/3yBImjOdd4
In some cases, almost 100% of the light energy can be converted to the second harmonic frequency. These cases typically involve intense pulsed laser beams passing through large crystals, and careful alignment to obtain phase matching.
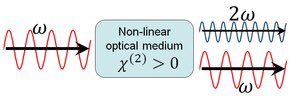
https://t.co/mzS7vVSREJ
https://t.co/353PdAX2fa
https://t.co/3yBImjOdd4
In some cases, almost 100% of the light energy can be converted to the second harmonic frequency. These cases typically involve intense pulsed laser beams passing through large crystals, and careful alignment to obtain phase matching.

More from Science
JUST ONE PERSON—UK 🇬🇧 scientists think one immunocompromised person who cleared virus slowly & only partially wiped out an infection, leaving behind genetically-hardier viruses that rebound & learn how to survive better. That’s likely how #B117 started. 🧵 https://t.co/bMMjM8Hiuz
2) The leading hypothesis is that the new variant evolved within just one person, chronically infected with the virus for so long it was able to evolve into a new, more infectious form.
same thing happened in Boston in another immunocompromised person that was sick for 155 days.
3) What happened in Boston with one 45 year old man who was highly infectious for 155 days straight before he died... is exactly what scientists think happened in Kent, England that gave rise to #B117.
4) Doctors were shocked to find virus has evolved many different forms inside of this one immunocompromised man. 20 new mutations in one virus, akin to the #B117. This is possibly how #B1351 in South Africa 🇿🇦 and #P1 in Brazil 🇧🇷 also evolved.
5) “On its own, the appearance of a new variant in genomic databases doesn’t tell us much. “That’s just one genome amongst thousands every week. It wouldn’t necessarily stick out,” says Oliver Pybus, a professor of evolution and infectious disease at Oxford.

2) The leading hypothesis is that the new variant evolved within just one person, chronically infected with the virus for so long it was able to evolve into a new, more infectious form.
same thing happened in Boston in another immunocompromised person that was sick for 155 days.
3) What happened in Boston with one 45 year old man who was highly infectious for 155 days straight before he died... is exactly what scientists think happened in Kent, England that gave rise to #B117.
Immunocompromised 45 year old suffered from #COVID19 for 155 days before he died. The virus was changing very quickly inside the man's body\u2014it acquired a big cluster of >20 mutations\u2014resembled the same ones seen in #B117 & #B1351. (NPR audio Part 1 of 2)\U0001f9f5https://t.co/7kWiBZ1xGk pic.twitter.com/ZJ7AExB78Y
— Eric Feigl-Ding (@DrEricDing) February 8, 2021
4) Doctors were shocked to find virus has evolved many different forms inside of this one immunocompromised man. 20 new mutations in one virus, akin to the #B117. This is possibly how #B1351 in South Africa 🇿🇦 and #P1 in Brazil 🇧🇷 also evolved.
2) NPR report audio part 2 of 2:
— Eric Feigl-Ding (@DrEricDing) February 8, 2021
Dr. Li couldn't believe what they found. "I was shocked," he says. "When I saw the virus sequences, I knew that we were dealing with something completely different and potentially very important." pic.twitter.com/HT3Yt6djFd
5) “On its own, the appearance of a new variant in genomic databases doesn’t tell us much. “That’s just one genome amongst thousands every week. It wouldn’t necessarily stick out,” says Oliver Pybus, a professor of evolution and infectious disease at Oxford.
You May Also Like
THREAD: 12 Things Everyone Should Know About IQ
1. IQ is one of the most heritable psychological traits – that is, individual differences in IQ are strongly associated with individual differences in genes (at least in fairly typical modern environments). https://t.co/3XxzW9bxLE
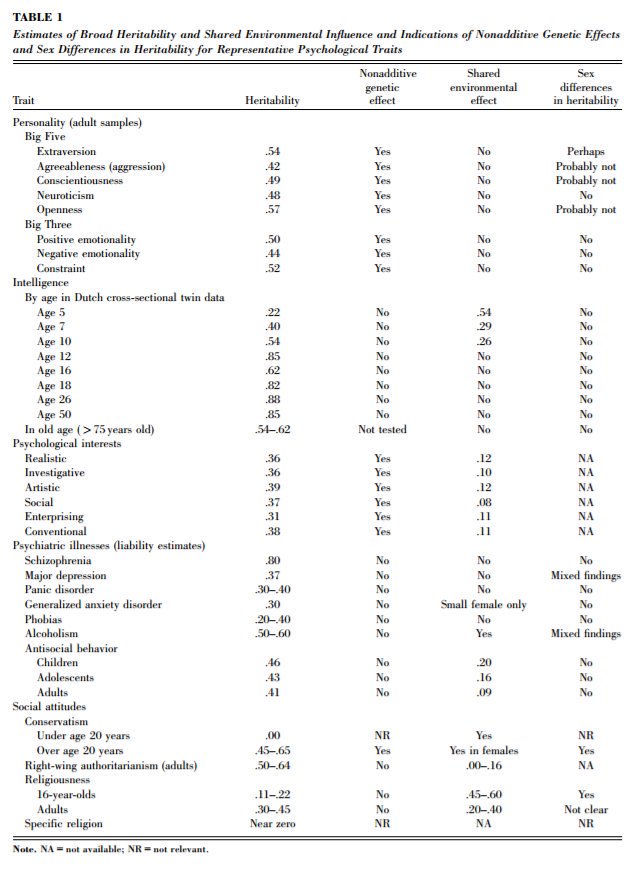
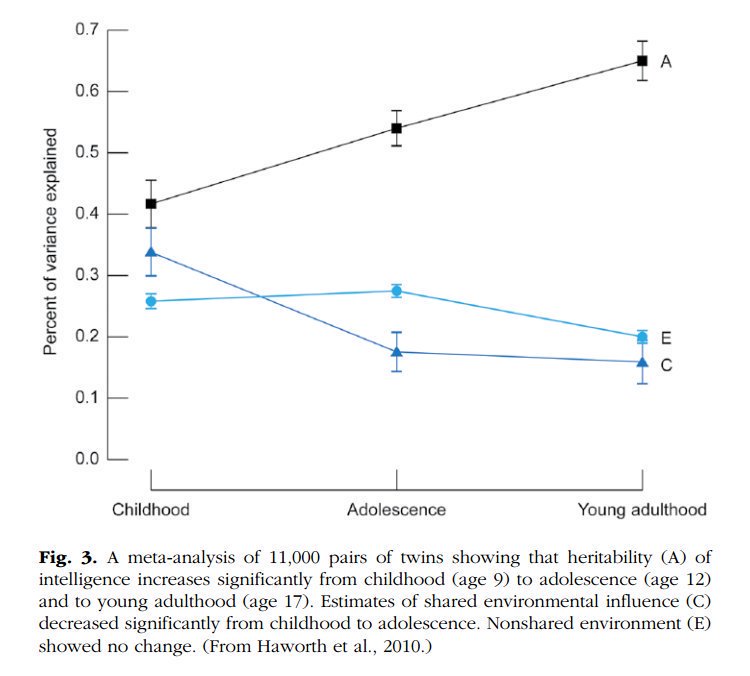
2. The heritability of IQ *increases* from childhood to adulthood. Meanwhile, the effect of the shared environment largely fades away. In other words, when it comes to IQ, nature becomes more important as we get older, nurture less. https://t.co/UqtS1lpw3n
3. IQ scores have been increasing for the last century or so, a phenomenon known as the Flynn effect. https://t.co/sCZvCst3hw (N ≈ 4 million)
(Note that the Flynn effect shows that IQ isn't 100% genetic; it doesn't show that it's 100% environmental.)

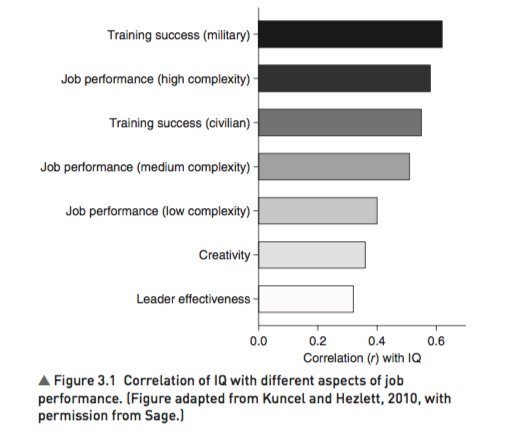
4. IQ predicts many important real world outcomes.
For example, though far from perfect, IQ is the single-best predictor of job performance we have – much better than Emotional Intelligence, the Big Five, Grit, etc. https://t.co/rKUgKDAAVx https://t.co/DWbVI8QSU3
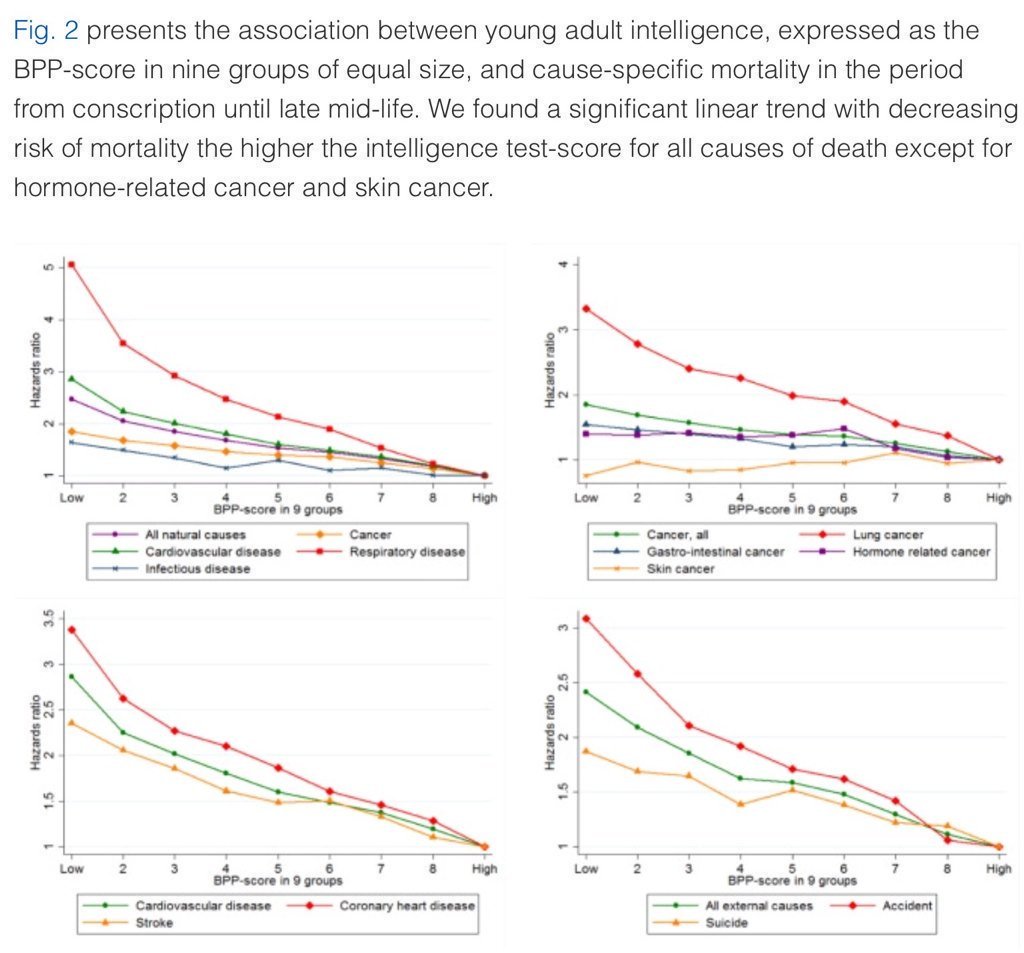
5. Higher IQ is associated with a lower risk of death from most causes, including cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, most forms of cancer, homicide, suicide, and accident. https://t.co/PJjGNyeQRA (N = 728,160)
1. IQ is one of the most heritable psychological traits – that is, individual differences in IQ are strongly associated with individual differences in genes (at least in fairly typical modern environments). https://t.co/3XxzW9bxLE

2. The heritability of IQ *increases* from childhood to adulthood. Meanwhile, the effect of the shared environment largely fades away. In other words, when it comes to IQ, nature becomes more important as we get older, nurture less. https://t.co/UqtS1lpw3n

3. IQ scores have been increasing for the last century or so, a phenomenon known as the Flynn effect. https://t.co/sCZvCst3hw (N ≈ 4 million)
(Note that the Flynn effect shows that IQ isn't 100% genetic; it doesn't show that it's 100% environmental.)

4. IQ predicts many important real world outcomes.
For example, though far from perfect, IQ is the single-best predictor of job performance we have – much better than Emotional Intelligence, the Big Five, Grit, etc. https://t.co/rKUgKDAAVx https://t.co/DWbVI8QSU3

5. Higher IQ is associated with a lower risk of death from most causes, including cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, most forms of cancer, homicide, suicide, and accident. https://t.co/PJjGNyeQRA (N = 728,160)