Not just Java, other languages (like python) were also released around/near 95, and also seemed to get to "mature" respect status. much quicker.
Java was first released in mid-1995, just 6 months before JS.
By 98, when I went to college, Java was already used for all the first level courses in the CS program.
How did it catch on so quickly (just 3 years) to shift university curriculum, which is usually so slow/behind?
Not just Java, other languages (like python) were also released around/near 95, and also seemed to get to "mature" respect status. much quicker.
it sure seems like the industry (and academics) just decided Java and C++ were the stable mature ones and langs like JS were toys.
Why wouldn't a university consider teaching JS alongside Java and C++ (and python), given they were all roughly the same age?
They're the "Java" and "C++" of today. They've been chosen.
More from Tech
The first area to focus on is diversity. This has become a dogma in the tech world, and despite the fact that tech is one of the most meritocratic industries in the world, there are constant efforts to promote diversity at the expense of fairness, merit and competency. Examples:
USC's Interactive Media & Games Division cancels all-star panel that included top-tier game developers who were invited to share their experiences with students. Why? Because there were no women on the
ElectronConf is a conf which chooses presenters based on blind auditions; the identity, gender, and race of the speaker is not known to the selection team. The results of that merit-based approach was an all-male panel. So they cancelled the conference.
Apple's head of diversity (a black woman) got in trouble for promoting a vision of diversity that is at odds with contemporary progressive dogma. (She left the company shortly after this
Also in the name of diversity, there is unabashed discrimination against men (especially white men) in tech, in both hiring policies and in other arenas. One such example is this, a developer workshop that specifically excluded men: https://t.co/N0SkH4hR35

USC's Interactive Media & Games Division cancels all-star panel that included top-tier game developers who were invited to share their experiences with students. Why? Because there were no women on the
ElectronConf is a conf which chooses presenters based on blind auditions; the identity, gender, and race of the speaker is not known to the selection team. The results of that merit-based approach was an all-male panel. So they cancelled the conference.
Apple's head of diversity (a black woman) got in trouble for promoting a vision of diversity that is at odds with contemporary progressive dogma. (She left the company shortly after this
Also in the name of diversity, there is unabashed discrimination against men (especially white men) in tech, in both hiring policies and in other arenas. One such example is this, a developer workshop that specifically excluded men: https://t.co/N0SkH4hR35

You May Also Like
Nano Course On Python For Trading
==========================
Module 1
Python makes it very easy to analyze and visualize time series data when you’re a beginner. It's easier when you don't have to install python on your PC (that's why it's a nano course, you'll learn python...
... on the go). You will not be required to install python in your PC but you will be using an amazing python editor, Google Colab Visit https://t.co/EZt0agsdlV
This course is for anyone out there who is confused, frustrated, and just wants this python/finance thing to work!
In Module 1 of this Nano course, we will learn about :
# Using Google Colab
# Importing libraries
# Making a Random Time Series of Black Field Research Stock (fictional)
# Using Google Colab
Intro link is here on YT: https://t.co/MqMSDBaQri
Create a new Notebook at https://t.co/EZt0agsdlV and name it AnythingOfYourChoice.ipynb
You got your notebook ready and now the game is on!
You can add code in these cells and add as many cells as you want
# Importing Libraries
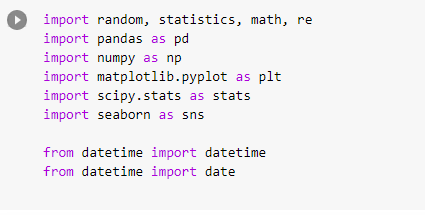
Imports are pretty standard, with a few exceptions.
For the most part, you can import your libraries by running the import.
Type this in the first cell you see. You need not worry about what each of these does, we will understand it later.
==========================
Module 1
Python makes it very easy to analyze and visualize time series data when you’re a beginner. It's easier when you don't have to install python on your PC (that's why it's a nano course, you'll learn python...
... on the go). You will not be required to install python in your PC but you will be using an amazing python editor, Google Colab Visit https://t.co/EZt0agsdlV
This course is for anyone out there who is confused, frustrated, and just wants this python/finance thing to work!
In Module 1 of this Nano course, we will learn about :
# Using Google Colab
# Importing libraries
# Making a Random Time Series of Black Field Research Stock (fictional)
# Using Google Colab
Intro link is here on YT: https://t.co/MqMSDBaQri
Create a new Notebook at https://t.co/EZt0agsdlV and name it AnythingOfYourChoice.ipynb
You got your notebook ready and now the game is on!
You can add code in these cells and add as many cells as you want
# Importing Libraries
Imports are pretty standard, with a few exceptions.
For the most part, you can import your libraries by running the import.
Type this in the first cell you see. You need not worry about what each of these does, we will understand it later.