It is astonishing that most of cognitive science ignores an obvious reality. That there are two kinds of humans.
More from Carlos E. Perez
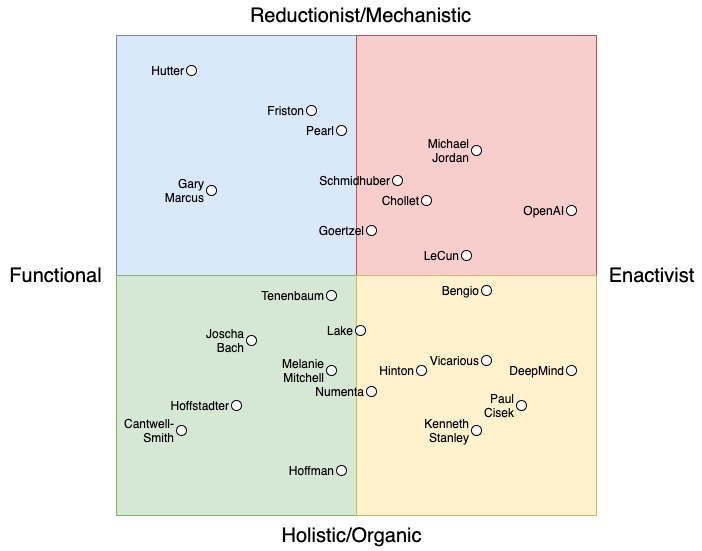
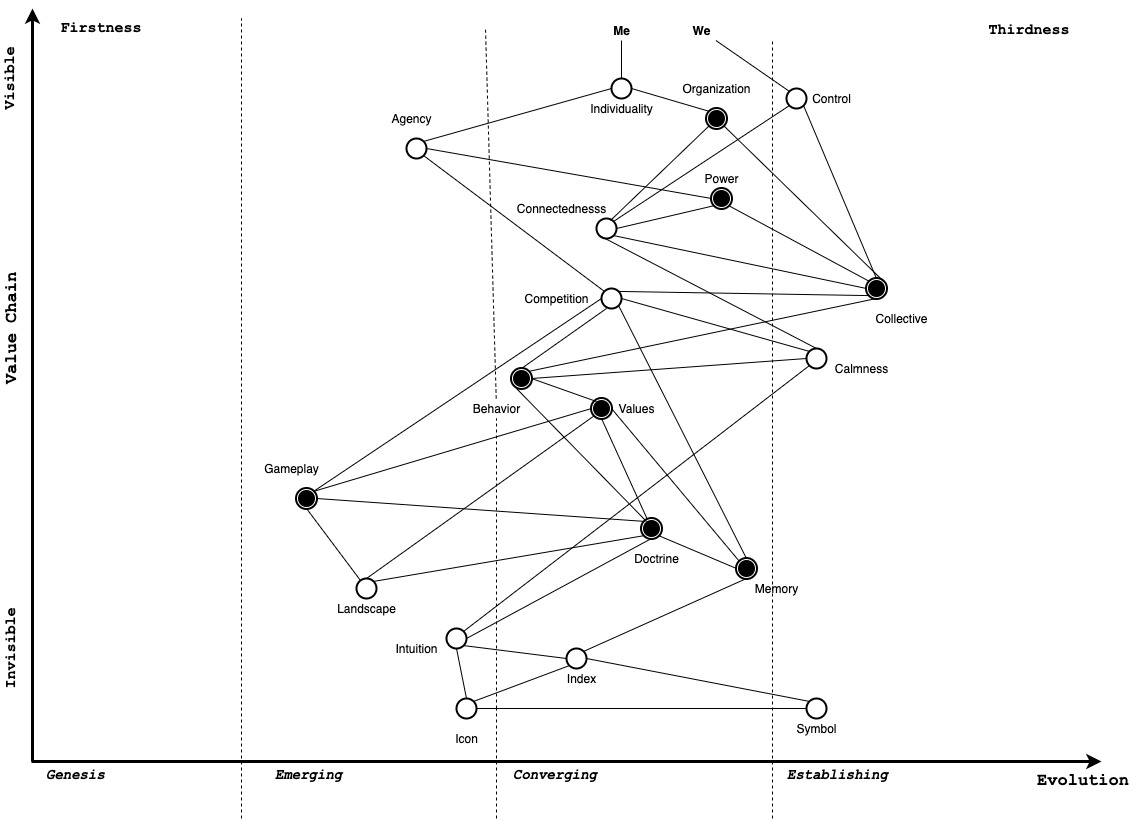
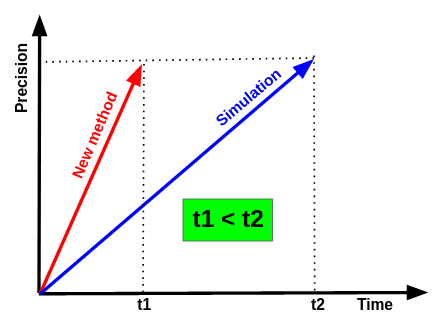
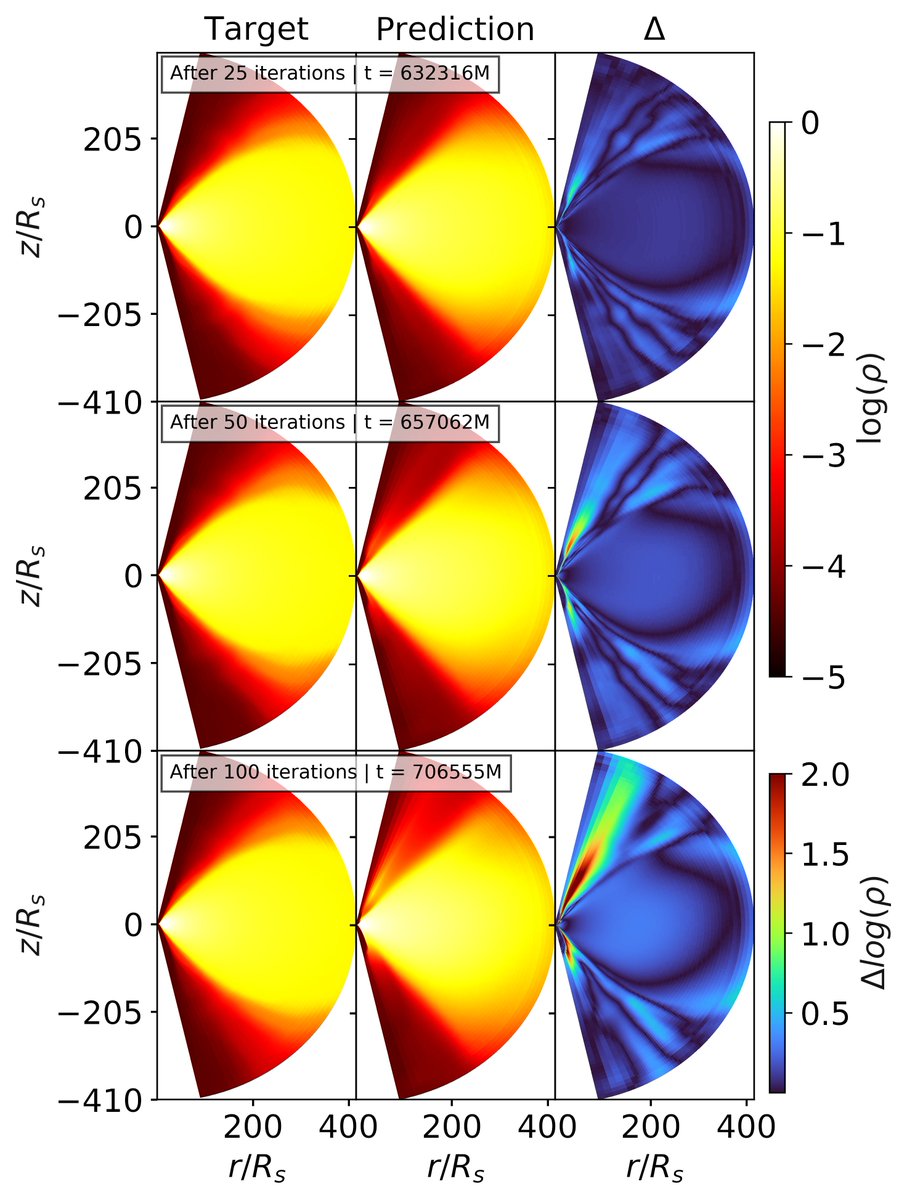
Programming in abstractions is very different from a system that is capable of its own 'abstracting'. But what does abstracting mean? We only know of its inputs and outputs, but we fail to describe its inner workings.
I like this short video about living in space. This is because it makes you realize the gaps in your knowledge when you turn off something (i.e. gravity) that you have always assumed to be present.
Perhaps we can understand 'abstracting' better if we turn of many assumptions that we unconsciously carry around. Perhaps we need to get rid of the excess baggage that is confusing our thinking about abstraction.
Turning off gravity and living in space is a perfect analogy. We somehow have to turn off a cognitive process to understand the meaning of abstraction.
The first step to divorce ourselves from our habitual cognitive processes is to realize the pervasiveness of 'noun-thinking' .
I like this short video about living in space. This is because it makes you realize the gaps in your knowledge when you turn off something (i.e. gravity) that you have always assumed to be present.
What does living in space do to the human body? pic.twitter.com/kzIlEEr7pp
— Tech Insider (@techinsider) December 20, 2020
Perhaps we can understand 'abstracting' better if we turn of many assumptions that we unconsciously carry around. Perhaps we need to get rid of the excess baggage that is confusing our thinking about abstraction.
Turning off gravity and living in space is a perfect analogy. We somehow have to turn off a cognitive process to understand the meaning of abstraction.
The first step to divorce ourselves from our habitual cognitive processes is to realize the pervasiveness of 'noun-thinking' .
More from Science
Hard agree. And if this is useful, let me share something that often gets omitted (not by @kakape).
Variants always emerge, & are not good or bad, but expected. The challenge is figuring out which variants are bad, and that can't be done with sequence alone.
You can't just look at a sequence and say, "Aha! A mutation in spike. This must be more transmissible or can evade antibody neutralization." Sure, we can use computational models to try and predict the functional consequence of a given mutation, but models are often wrong.
The virus acquires mutations randomly every time it replicates. Many mutations don't change the virus at all. Others may change it in a way that have no consequences for human transmission or disease. But you can't tell just looking at sequence alone.
In order to determine the functional impact of a mutation, you need to actually do experiments. You can look at some effects in cell culture, but to address questions relating to transmission or disease, you have to use animal models.
The reason people were concerned initially about B.1.1.7 is because of epidemiological evidence showing that it rapidly became dominant in one area. More rapidly that could be explained unless it had some kind of advantage that allowed it to outcompete other circulating variants.
Variants always emerge, & are not good or bad, but expected. The challenge is figuring out which variants are bad, and that can't be done with sequence alone.
Feels like the next thing we're going to need is a ranking system for how concerning "variants of concern\u201d actually are.
— Kai Kupferschmidt (@kakape) January 15, 2021
A lot of constellations of mutations are concerning, but people are lumping together variants with vastly different levels of evidence that we need to worry.
You can't just look at a sequence and say, "Aha! A mutation in spike. This must be more transmissible or can evade antibody neutralization." Sure, we can use computational models to try and predict the functional consequence of a given mutation, but models are often wrong.
The virus acquires mutations randomly every time it replicates. Many mutations don't change the virus at all. Others may change it in a way that have no consequences for human transmission or disease. But you can't tell just looking at sequence alone.
In order to determine the functional impact of a mutation, you need to actually do experiments. You can look at some effects in cell culture, but to address questions relating to transmission or disease, you have to use animal models.
The reason people were concerned initially about B.1.1.7 is because of epidemiological evidence showing that it rapidly became dominant in one area. More rapidly that could be explained unless it had some kind of advantage that allowed it to outcompete other circulating variants.
I want to share my thoughts, as someone who has been so alarmed by the so-called "dissident" scientists like Gupta, Heneghan, Kuldorff, Bhattacharya, & Ioannidis who consider themselves brave Galileos unfairly treated by "establishment scientists." I will try not to swear. 1/n
I want to talk about 3 things:
‼️Their fringe views are inhumane, unethical junk science that promotes harm
‼️They complain that they've been marginalized but this is simply untrue
‼️I am sick of people telling me we have to "listen to both sides." There aren't 2 sides here 2/n
These 'dissident' scientists have consistently downplayed COVID-19, urging policymakers not to take aggressive control measures. They claim it is not a serious threat. Gupta even went on TV saying people under 65 shouldn't worry about it!
RECEIPTS
They have consistently argued that policymakers should just let the virus rip, in an attempt to reach herd immunity by natural infection. Kuldorff *continues* to argue for this even now that we have many highly effective, safe vaccines.
We've never controlled a deadly, contagious pandemic before by just letting the virus spread, as this approach kills & disables too many people. In Manaus, Brazil, 66% of the city was infected & an astonishing *1 in 500* people died of COVID-19
If this is true raises the question of why certain (fringe & unethical) views got access to No.10 while others were ignored... https://t.co/A75HrSEqo4
— Prof. Devi Sridhar (@devisridhar) December 13, 2020
I want to talk about 3 things:
‼️Their fringe views are inhumane, unethical junk science that promotes harm
‼️They complain that they've been marginalized but this is simply untrue
‼️I am sick of people telling me we have to "listen to both sides." There aren't 2 sides here 2/n
These 'dissident' scientists have consistently downplayed COVID-19, urging policymakers not to take aggressive control measures. They claim it is not a serious threat. Gupta even went on TV saying people under 65 shouldn't worry about it!
RECEIPTS
They have consistently argued that policymakers should just let the virus rip, in an attempt to reach herd immunity by natural infection. Kuldorff *continues* to argue for this even now that we have many highly effective, safe vaccines.
Focused Protection: The Middle Ground between Lockdowns and "Let-it-rip". An essay by Jay Bhattacharya (@Stanford), @SunetraGupta (@UniofOxford) and @MartinKulldorff (@Harvard). https://t.co/T8uLxSFwgh
— Martin Kulldorff (@MartinKulldorff) December 11, 2020
We've never controlled a deadly, contagious pandemic before by just letting the virus spread, as this approach kills & disables too many people. In Manaus, Brazil, 66% of the city was infected & an astonishing *1 in 500* people died of COVID-19