The endangered whales must contend with up to 1,000 boats moving daily through an important feeding area in the eastern South Pacific, according to research published in the scientific journal Nature.@WeDontHaveTime
#ForNature @JohnKerry
Blue whales threatened by ship collisions in busy Patagonia waters
— James Mitchell \u24cb\U0001f42c (@MesMitch) February 1, 2021
Endangered giants face potentially fatal encounters with the 1,000 daily fishing vessels moving through main feeding area off Chile, scientists warn\U0001f43b\u200d\u2744\ufe0f@WeDontHaveTime
#ForNature @JohnKerry
More from Science
It's time, my friends 🤩🤩
[Thread] #ProjectOdin
The Alliance has Project Odin ready to go - the new quantum-based internet. #ElonMusk #QVS #QFS #ProjectOdin
— Der Preu\xdfe Parler: @DerPreusse (@DerPreusse1963) January 12, 2021
https://t.co/fO90N78fta
new quantum-based internet #ElonMusk #QVS #QFS
Political justification ⏬⏬
#ProjectOdin
#ProjectOdin #Starlink #ElonMusk #QuantumInternet
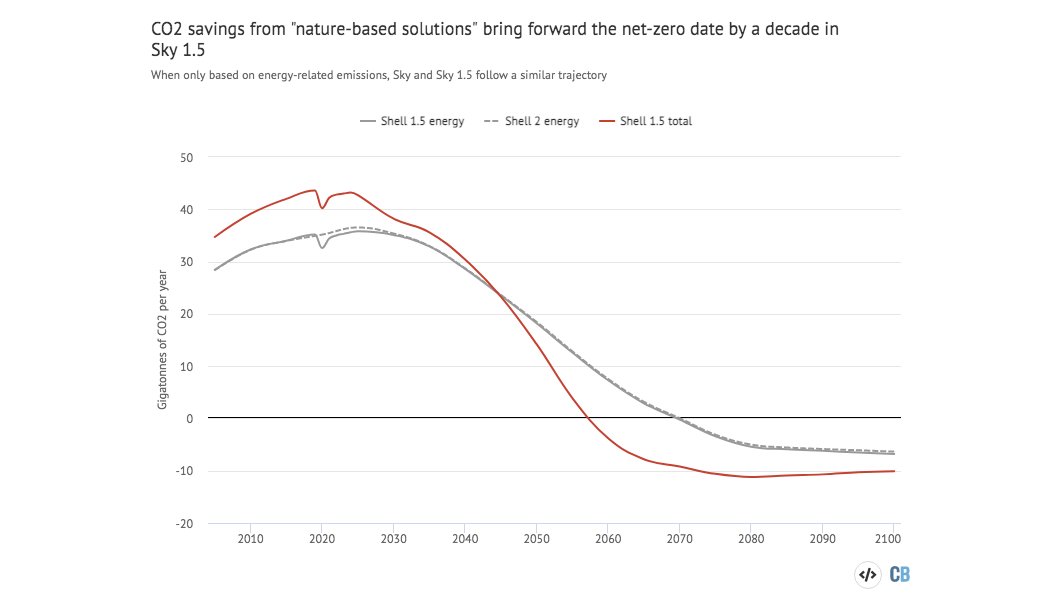
Oil, gas, coal, solar.... all basically unchanged.
The key difference: A new forest the size of Brazil to suck up the extra CO2.
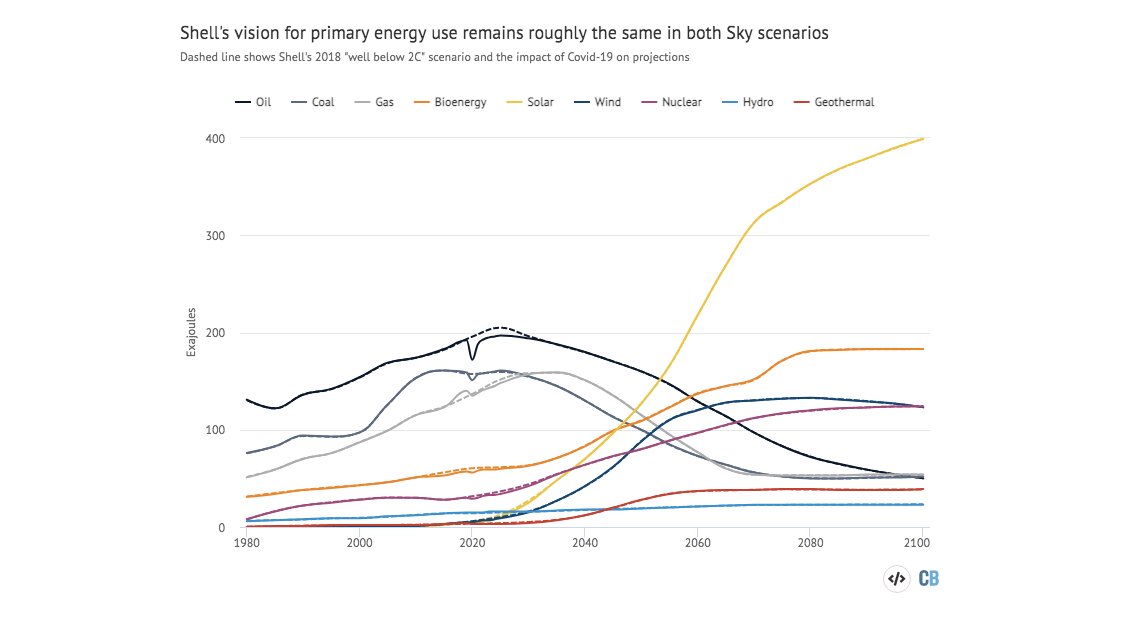
Including "nature-based solutions" in the outlook brings forward the date for net-zero emissions to 2058.
Without them their pathway for CO2 emissions is the same as the previous one.
(It's also towards the higher end of 1.5C emissions pathways.)
The "Brazil-sized" forest idea isn't actually new, it has been kicking around for a couple of years.
It was referenced in the "well-below 2C" scenario although not formally included in it, and Shell's CEO has been framing it as the only viable way of getting to 1.5C.

Fine, but who is going to plant all those trees? Well... Shell says it will plant some of them.
Only yesterday Shell said forests were a key part of its net-zero strategy.
Not everyone is convinced though
https://t.co/RaJm7tOHxb
Shell plans to use forests to remove 120 Mt/yr of CO2 by 2030.
— Greg Muttitt (@FuelOnTheFire) February 12, 2021
Appropriate land for forestation is finite, and risks competition with food production and human rights of current land owners/users, esp Indigenous
Given that Shell's 1.5C scenario also sees a big scaling up of bioenergy, the question remains: where are all those trees and bioenergy crops going to go?

I find it remarkable that a section of society not rejoicing that children very rarely ill with COVID compared to other viruses and much less infectious than adults
— Michael Absoud \U0001f499 (@MAbsoud) February 12, 2021
Instead trying prove the opposite!
Why??
2. @c_drosten has talked about this extensively and @dgurdasani1 and @DrZoeHyde have repeatedly pointed out flaws in the studies which have purported to show this. Now for the other assertion: children are very rarely ill with COVID19.
3. Children seem to suffer less with acute illness, but we have no idea of the long-term impact of infection. We do know #LongCovid affects some children. @LongCovidKids now speaks for 1,500 children struggling with a wide range of long-term symptoms.
4. 1,500 children whose parents found a small campaign group. How many more are out there? We don’t know. ONS data suggests there might be many, but the issue hasn’t been studied sufficiently well or long enough for a definitive answer.
5. Some people have talked about #COVID19 being this generation’s Polio. According to US CDC, Polio resulted in inapparent infection in more than 99% of people. Severe disease occurred in a tiny fraction of those infected. Source: