Mollyycolllinss Categories Economy
7 days
30 days
All time
Recent
Popular
1/OK, let's take a little break from Coup Twitter, and think about an economic issue:
How can we build up the wealth of the middle class?
2/The typical American has surprisingly little wealth compared to the typical resident of many other developed countries.
This is a fact that is not widely known or appreciated.
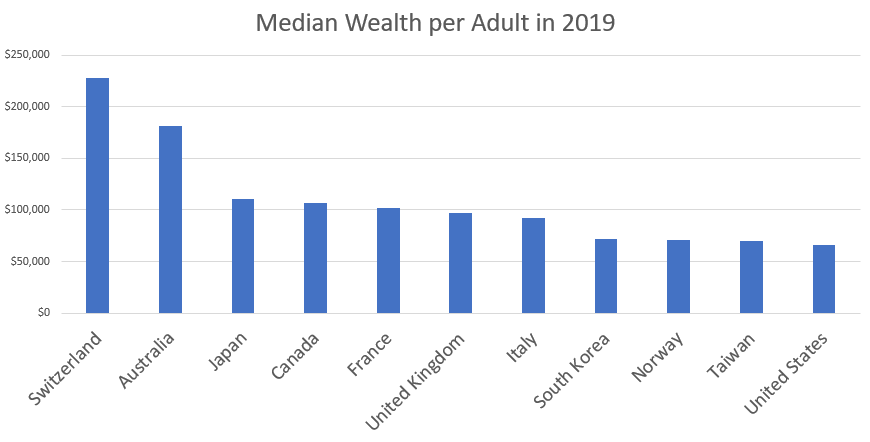
3/Now, some people argue that stuff like Social Security or social insurance programs should be included in wealth. But I chose to focus on private wealth because I think having assets you can sell whenever you want is important to
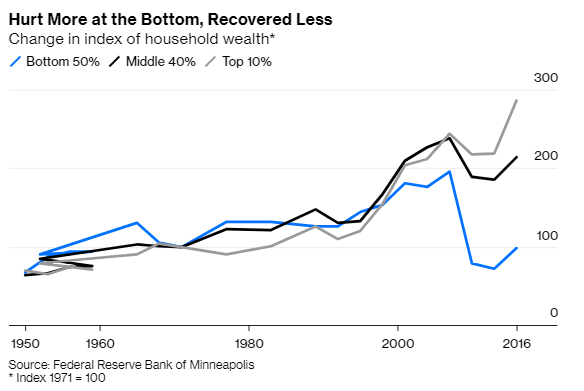
4/For many decades after World War 2, middle-class wealth in America was on a smooth upward trajectory.
Then the housing crash came, and all that changed. Suddenly the rich were still doing well but everyone else was seeing the end of their American Dream.
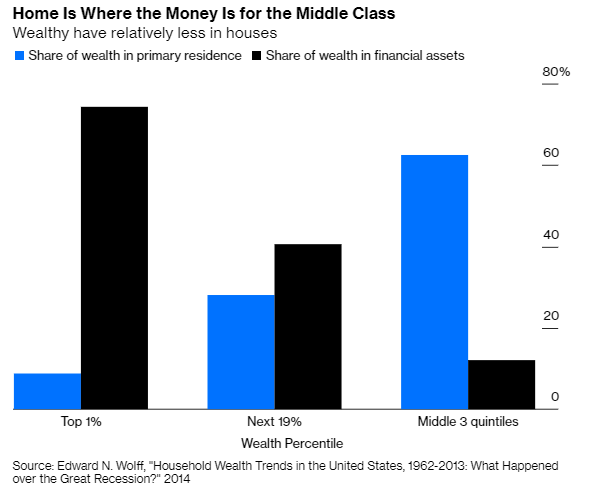
5/Why the divergence?
Because the American middle class has its wealth in houses -- specifically, in the houses they live in.
It's the rich who own stocks.
How can we build up the wealth of the middle class?
2/The typical American has surprisingly little wealth compared to the typical resident of many other developed countries.
This is a fact that is not widely known or appreciated.

3/Now, some people argue that stuff like Social Security or social insurance programs should be included in wealth. But I chose to focus on private wealth because I think having assets you can sell whenever you want is important to
Yes, these numbers don't include things like Social Security, just privately held wealth. They're not an attempt to capitalize every possible future income stream.
— Noahtogolpe \U0001f407 (@Noahpinion) January 10, 2021
4/For many decades after World War 2, middle-class wealth in America was on a smooth upward trajectory.
Then the housing crash came, and all that changed. Suddenly the rich were still doing well but everyone else was seeing the end of their American Dream.

5/Why the divergence?
Because the American middle class has its wealth in houses -- specifically, in the houses they live in.
It's the rich who own stocks.

Some people want us to believe there's not enough solar energy available to cover our worldwide energy needs
They often use EROI (Energy Return On Investment) as their metric
This is a rant against these EROI people misinforming the debate, based on a rebuttal of a 2020 paper

In essence the approach of the paper is straightforward:
1) Discard water and 96% of land because it's supposedly unavailable
2) Assume solar cells on just 1/5th of the remaining 4%
3) Complain that production of solar panels takes a lot of
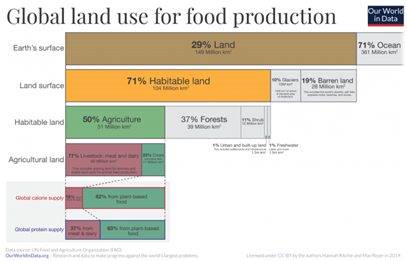
About 1) (available land)
Discarding 96% of land seems pretty extreme:
30% of the world's land is barren
40% of the world's land is used for meat
I think we could find more than 4% if we tried
(but we don't have to: we need less than 1%)
https://t.co/rJZiNWcu7F
About 2) (using 1/5th of available land)
If cells are expensive and land is dirt cheap, covering 20% with solar cells is logical
But with cheap cells you maximize land use: 80% is easily possible
New paper headline:
"Global available solar energy over 10 times what we need"

About 3) (20% of energy is needed for production)
This is something @MLiebreich and I often complain about:
If you get more energy out than you put it, that's FINE
If you get five times more energy out, that's GREAT
EROI is a USELESS metric. Let's STOP using it. At all.
They often use EROI (Energy Return On Investment) as their metric
This is a rant against these EROI people misinforming the debate, based on a rebuttal of a 2020 paper

In essence the approach of the paper is straightforward:
1) Discard water and 96% of land because it's supposedly unavailable
2) Assume solar cells on just 1/5th of the remaining 4%
3) Complain that production of solar panels takes a lot of
About 1) (available land)
Discarding 96% of land seems pretty extreme:
30% of the world's land is barren
40% of the world's land is used for meat
I think we could find more than 4% if we tried
(but we don't have to: we need less than 1%)
https://t.co/rJZiNWcu7F

About 2) (using 1/5th of available land)
If cells are expensive and land is dirt cheap, covering 20% with solar cells is logical
But with cheap cells you maximize land use: 80% is easily possible
New paper headline:
"Global available solar energy over 10 times what we need"

About 3) (20% of energy is needed for production)
This is something @MLiebreich and I often complain about:
If you get more energy out than you put it, that's FINE
If you get five times more energy out, that's GREAT
EROI is a USELESS metric. Let's STOP using it. At all.
What a year: 203 essays about degrowth in English since the beginning of March. Here is a selection of some of my favourites. Thank you @fem_degrowth, @beth_stratford, @thedownshifters, @corbinkbarthold, @degrowth_info for these brilliant texts.
THREAD/
https://t.co/1lFaJM52RX
https://t.co/i5HOfZ19r7
https://t.co/DuPSrrqnzz
https://t.co/0ANveWdvFO
THREAD/
https://t.co/1lFaJM52RX
https://t.co/i5HOfZ19r7
https://t.co/DuPSrrqnzz
https://t.co/0ANveWdvFO
1/ To add a little texture to @NickHanauer's thread, it's important to recognize that there's a good reason why orthodox economists (& economic cosplayers) so vehemently oppose a $15 min wage:
The min wage is a wedge that threatens to undermine all of orthodox economic theory.
2/ Orthodox economics is grounded in two fundamental models: a systems model that describes the market as a closed equilibrium system, and a behavioral model that describes humans as rational, self-interested utility-maximizers. The modern min wage debate undermines both models.
3/ The assertion that a min wage kills jobs is so central to orthodox economics that it is often used as the textbook example of the Supply/Demand curve. Raise the cost of labor and businesses will buy less of it. It's literally Econ 101!
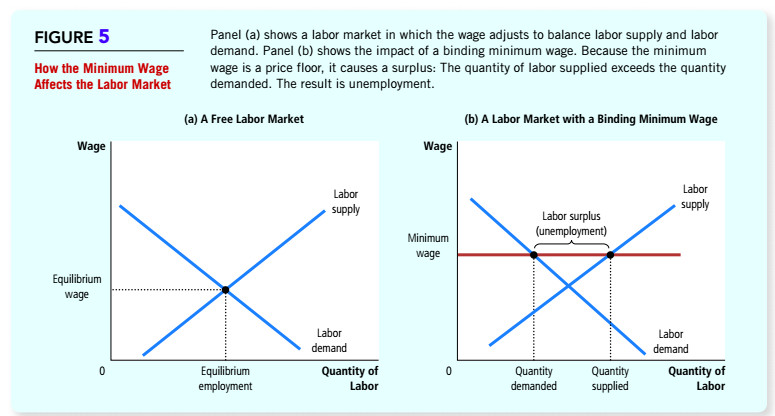
4/ Econ 101 insists that markets automatically set an efficient "equilibrium price" for labor & everything else. Mess with this price and bad things happen. Yet decades of empirical research has persuaded a majority of economists that this just isn't
5/ How can this be? Well, either the market is not a closed equilibrium system in which if you raise the price of labor employers automatically purchase less of it... OR the market is not automatically setting an efficient and fair equilibrium wage. Or maybe both. #FAIL
The min wage is a wedge that threatens to undermine all of orthodox economic theory.
1/4 Most people, especially academic economists, think that the controversy over the minimum wage is a contest over facts. It's not. It's a contest over power, status, and wealth. It is just like the contest over racial and gender justice.
— Nick Hanauer (@NickHanauer) January 17, 2021
2/ Orthodox economics is grounded in two fundamental models: a systems model that describes the market as a closed equilibrium system, and a behavioral model that describes humans as rational, self-interested utility-maximizers. The modern min wage debate undermines both models.
3/ The assertion that a min wage kills jobs is so central to orthodox economics that it is often used as the textbook example of the Supply/Demand curve. Raise the cost of labor and businesses will buy less of it. It's literally Econ 101!

4/ Econ 101 insists that markets automatically set an efficient "equilibrium price" for labor & everything else. Mess with this price and bad things happen. Yet decades of empirical research has persuaded a majority of economists that this just isn't
5/ How can this be? Well, either the market is not a closed equilibrium system in which if you raise the price of labor employers automatically purchase less of it... OR the market is not automatically setting an efficient and fair equilibrium wage. Or maybe both. #FAIL
One of the hardest problems post-pandemic will be how to revive so-called "left behind" places.
Post-industrial towns, run-down suburbs, coastal communities - these places were already struggling before the crisis and have fared worst in the last year.
What should we do?
Today, @ukonward sets out the beginning of a plan to repair our social fabric. It follows our extensive research over the last year, expertly chaired by @jamesosh, and funded by @jrf_uk, @Shelter and @peoplesbiz.
https://t.co/d3T5uPwG9N

Before I get into recommendations, some findings from previous Onward research.
In 2018, we found 71% of people believe "community has declined in my lifetime"
In 2019, we found 65% would rather live in “a society that focuses on giving people more security” vs 35% for freedom

This was the basis for our identification of 'Workington Man' as the archetypal swing voter in 2019, and led us to predict (correctly) that large numbers of Red Wall seats could fall. A key driver was a desire for security, belonging and pride in place.

There is also a key regional dimension to this. We also tested people's affinity with the UK's direction of travel, across both cultural and economic dimensions - revealing the extraordinary spread below: London vs. the Rest.
https://t.co/HrorW4xaLp

Post-industrial towns, run-down suburbs, coastal communities - these places were already struggling before the crisis and have fared worst in the last year.
What should we do?
Today, @ukonward sets out the beginning of a plan to repair our social fabric. It follows our extensive research over the last year, expertly chaired by @jamesosh, and funded by @jrf_uk, @Shelter and @peoplesbiz.
https://t.co/d3T5uPwG9N

Before I get into recommendations, some findings from previous Onward research.
In 2018, we found 71% of people believe "community has declined in my lifetime"
In 2019, we found 65% would rather live in “a society that focuses on giving people more security” vs 35% for freedom

This was the basis for our identification of 'Workington Man' as the archetypal swing voter in 2019, and led us to predict (correctly) that large numbers of Red Wall seats could fall. A key driver was a desire for security, belonging and pride in place.

There is also a key regional dimension to this. We also tested people's affinity with the UK's direction of travel, across both cultural and economic dimensions - revealing the extraordinary spread below: London vs. the Rest.
https://t.co/HrorW4xaLp




















