#MadagascarFrogs
It's another stunning Malagasy #dartfrog/#poisonfrog for today's #FrogOfTheDay, #42 Mantella cowani Boulenger, 1882! A highly threatened, actively conserved and managed frog from the highlands of central #Madagascar
#MadagascarFrogs
📸D.Edmonds/CalPhotos

#MadagascarFrogs
#MadagascarFrogs

#MadagascarFrogs
https://t.co/dwaHMbrYbj

#MadagascarFrogs
📸B.Freiermuth/CalPhotos

#MadagascarFrogs
📸Mantella cowanii Action Plan, 2021–2025 (on which more below)
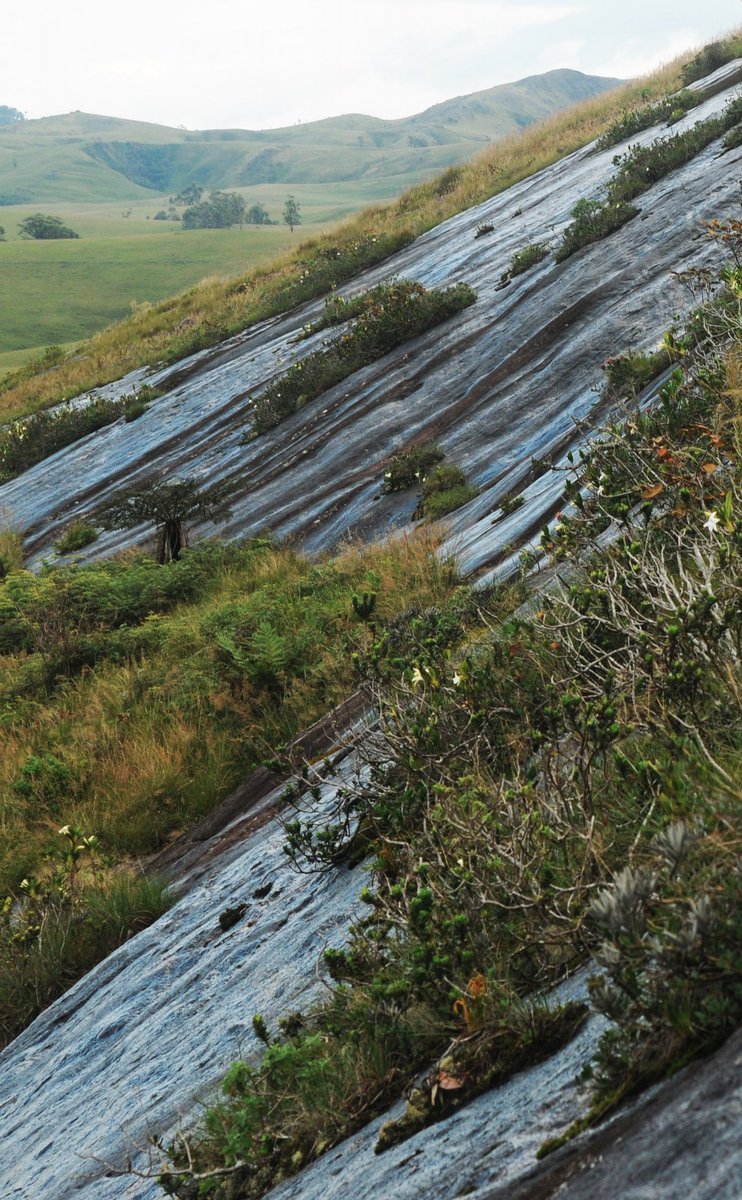

#MadagascarFrogs
https://t.co/VMFGZ7tP0Y
https://t.co/9uFZ7KBRzZ
https://t.co/gJXip5xMTv
#MadagascarFrogs
#MadagascarFrogs
https://t.co/SAON3F2VqF
#MadagascarFrogs
#MadagascarFrogs
https://t.co/ozm89CMSSR

More from Science
All modern research questions frame your mindset and self-frame research paradigm. Broad thinking: how little of everything can a citizen survive on; how cheap can your upkeep be? /1
When an American patient lands in an Austrian hospital for a back problem, a doctor tells him to perform a set of exercises.
- How many?
- Do you have anything else to do? /2
This interchange illustrates two mindsets colliding at bedside. How little can I get away with vs there is no limit to effort when it comes to your wellness. /3
When you were robbed of movement, somebody started selling you exercise. To understand that digging a ditch, to build a house, or to carry a child around, or waking to your grandparents for an hour is not the same as jogging on a treadmill... will reveal what research hides.
/4
When I talk about doing a purposeful activity outdoors, I look at complexity of movement, purpose, meaning, sun, and air, even an opportunity to meet a neighbor... that is now reduced to a calcium pill, vitamin D, an antidepressant, an osteoporosis shot, and an oxygen tank. /5
Is moderate exercise enough to live as long as possible, or should you be doing vigorous exercise? And what proportion is best? This article has the answers. https://t.co/YJqpaaI0UR
— Sebastian Rushworth M.D. (@sebrushworth) January 24, 2021
When an American patient lands in an Austrian hospital for a back problem, a doctor tells him to perform a set of exercises.
- How many?
- Do you have anything else to do? /2
This interchange illustrates two mindsets colliding at bedside. How little can I get away with vs there is no limit to effort when it comes to your wellness. /3
When you were robbed of movement, somebody started selling you exercise. To understand that digging a ditch, to build a house, or to carry a child around, or waking to your grandparents for an hour is not the same as jogging on a treadmill... will reveal what research hides.
/4
When I talk about doing a purposeful activity outdoors, I look at complexity of movement, purpose, meaning, sun, and air, even an opportunity to meet a neighbor... that is now reduced to a calcium pill, vitamin D, an antidepressant, an osteoporosis shot, and an oxygen tank. /5
You May Also Like
https://t.co/6cRR2B3jBE
Viruses and other pathogens are often studied as stand-alone entities, despite that, in nature, they mostly live in multispecies associations called biofilms—both externally and within the host.
https://t.co/FBfXhUrH5d

Microorganisms in biofilms are enclosed by an extracellular matrix that confers protection and improves survival. Previous studies have shown that viruses can secondarily colonize preexisting biofilms, and viral biofilms have also been described.

...we raise the perspective that CoVs can persistently infect bats due to their association with biofilm structures. This phenomenon potentially provides an optimal environment for nonpathogenic & well-adapted viruses to interact with the host, as well as for viral recombination.

Biofilms can also enhance virion viability in extracellular environments, such as on fomites and in aquatic sediments, allowing viral persistence and dissemination.

Viruses and other pathogens are often studied as stand-alone entities, despite that, in nature, they mostly live in multispecies associations called biofilms—both externally and within the host.
https://t.co/FBfXhUrH5d

Microorganisms in biofilms are enclosed by an extracellular matrix that confers protection and improves survival. Previous studies have shown that viruses can secondarily colonize preexisting biofilms, and viral biofilms have also been described.

...we raise the perspective that CoVs can persistently infect bats due to their association with biofilm structures. This phenomenon potentially provides an optimal environment for nonpathogenic & well-adapted viruses to interact with the host, as well as for viral recombination.

Biofilms can also enhance virion viability in extracellular environments, such as on fomites and in aquatic sediments, allowing viral persistence and dissemination.

Took me 5 years to get the best Chartink scanners for Stock Market, but you’ll get it in 5 mminutes here ⏰
Do Share the above tweet 👆
These are going to be very simple yet effective pure price action based scanners, no fancy indicators nothing - hope you liked it.
https://t.co/JU0MJIbpRV
52 Week High
One of the classic scanners very you will get strong stocks to Bet on.
https://t.co/V69th0jwBr
Hourly Breakout
This scanner will give you short term bet breakouts like hourly or 2Hr breakout
Volume shocker
Volume spurt in a stock with massive X times
Do Share the above tweet 👆
These are going to be very simple yet effective pure price action based scanners, no fancy indicators nothing - hope you liked it.
https://t.co/JU0MJIbpRV
52 Week High
One of the classic scanners very you will get strong stocks to Bet on.
https://t.co/V69th0jwBr
Hourly Breakout
This scanner will give you short term bet breakouts like hourly or 2Hr breakout
Volume shocker
Volume spurt in a stock with massive X times