Technology is connected to the "tailpipes" of these facilities and is used to remove CO2 from the plant exhaust.
What is carbon capture? And how does it work?
While carbon capture is regularly discussed in the media, no one really ever explains what it is.
Below is a quick thread discussing the technology behind traditional carbon capture 👇
Technology is connected to the "tailpipes" of these facilities and is used to remove CO2 from the plant exhaust.
This step is called "sequestration" and is why experts often talks about "carbon capture and sequestration" or "CCS".
Currently, one of the most economic forms of carbon capture is called "amine-based" capture.
An "amine" is a special liquid chemical which selectively grabs on to CO2 molecules.
The exhaust bubbles up through the column, and the amine drips down.
The liquid amine and gas exhaust mix in the column.
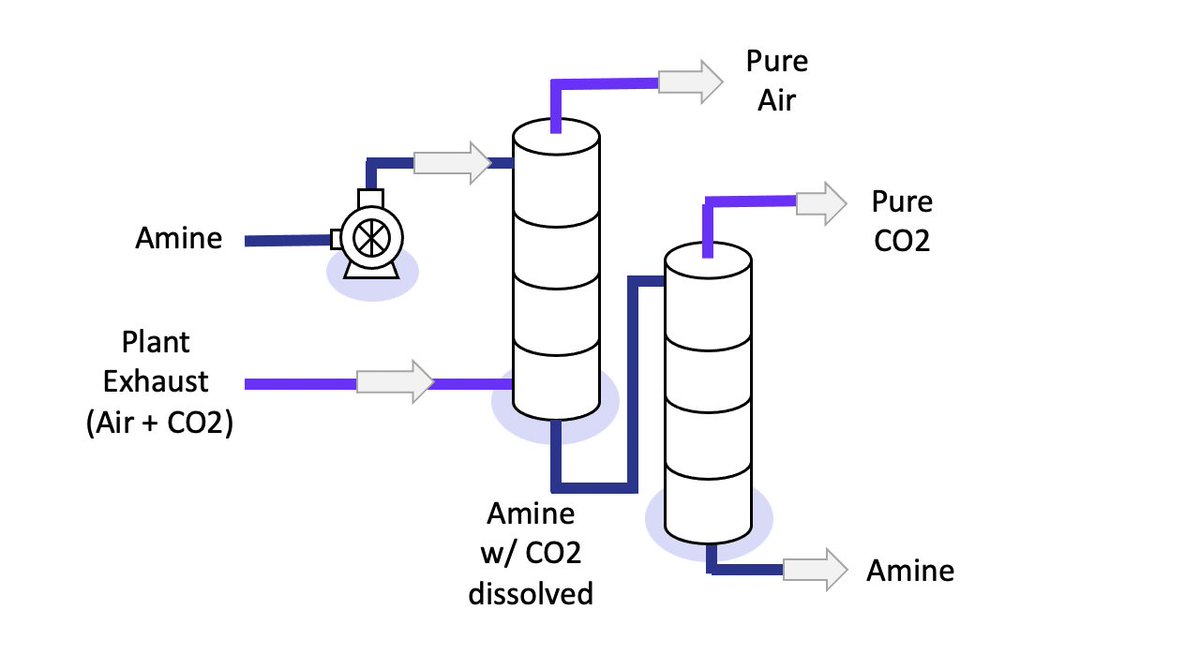
The amine with dissolved CO2 is sent into a second column where it is heated.
In the second column, the CO2 pops out of the amine.
Now, we have separated the CO2.
Below is a picture of an amine plant used for CO2 scrubbing.
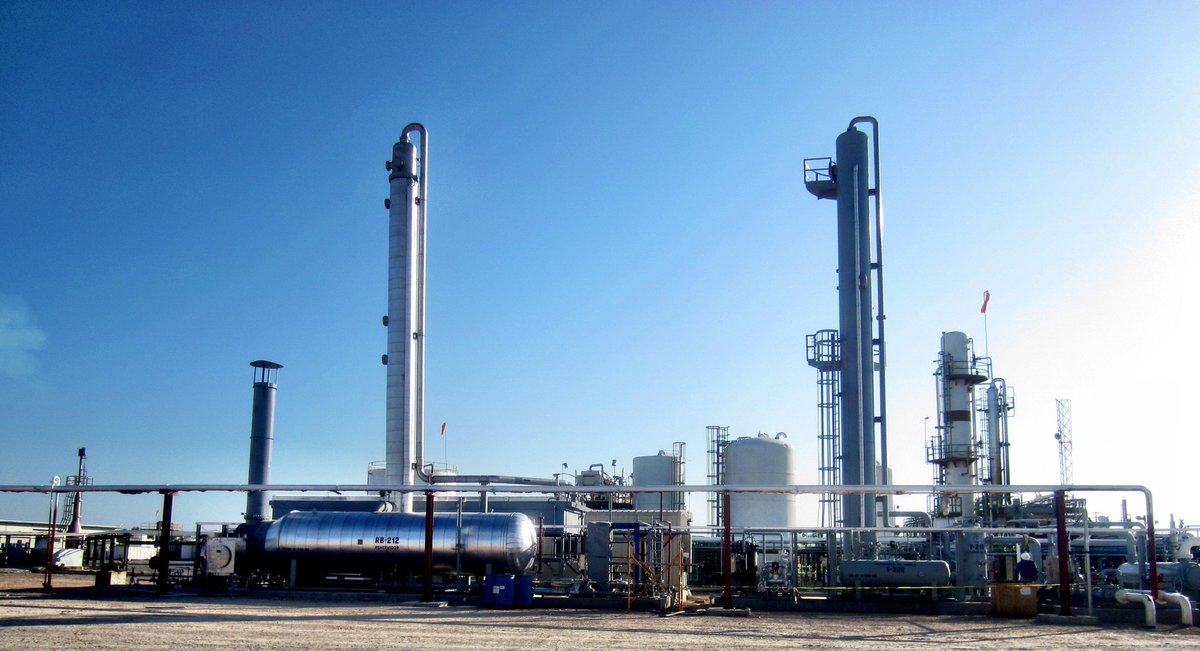

The CO2 is injected into a well for permanent storage underground, usually a few hundred yards away.
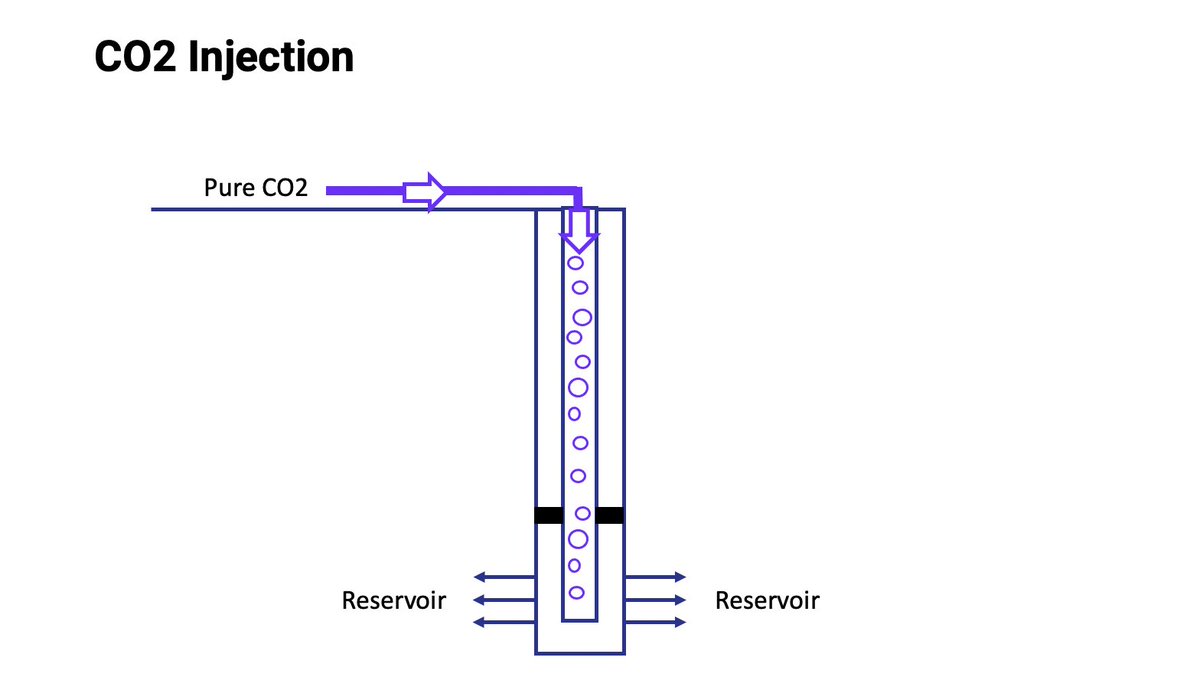
What I've described is called "point source capture" because it captures CO2 from a single plant exhaust
With new advances in technology, CO2 can also be captured directly from the air we breathe