⬇️⬇️⬇️ The "Math" of Fear
As it is Thursday, I have a post for you today in anticipation of Gov. DeWine's new Maps of Fear which he has tried to phase in. I have previously discussed both the new red and blue maps and their issues -
The first is a hyper-simplistic (and unrealistic) but illustrative example of the calculations that the new blue map goes through to arrive at its numbers.
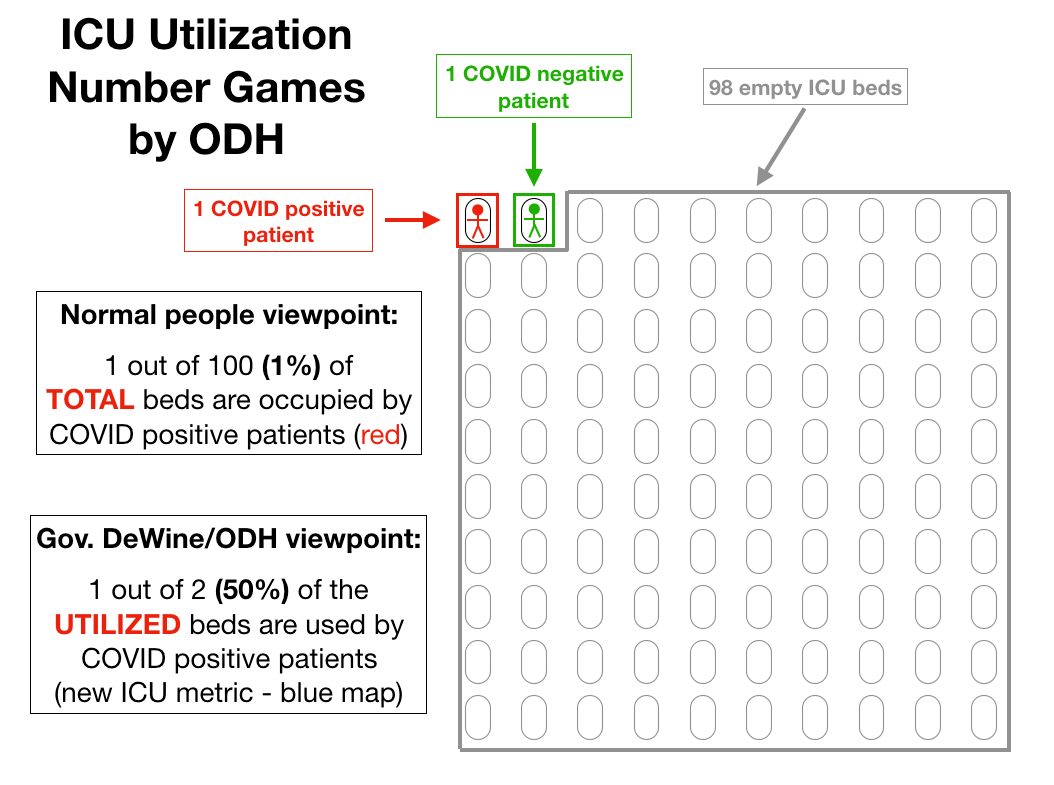
But that's not how Gov. DeWine would present this situation to us. Instead of looking at the total available beds, they look only at the beds in use.
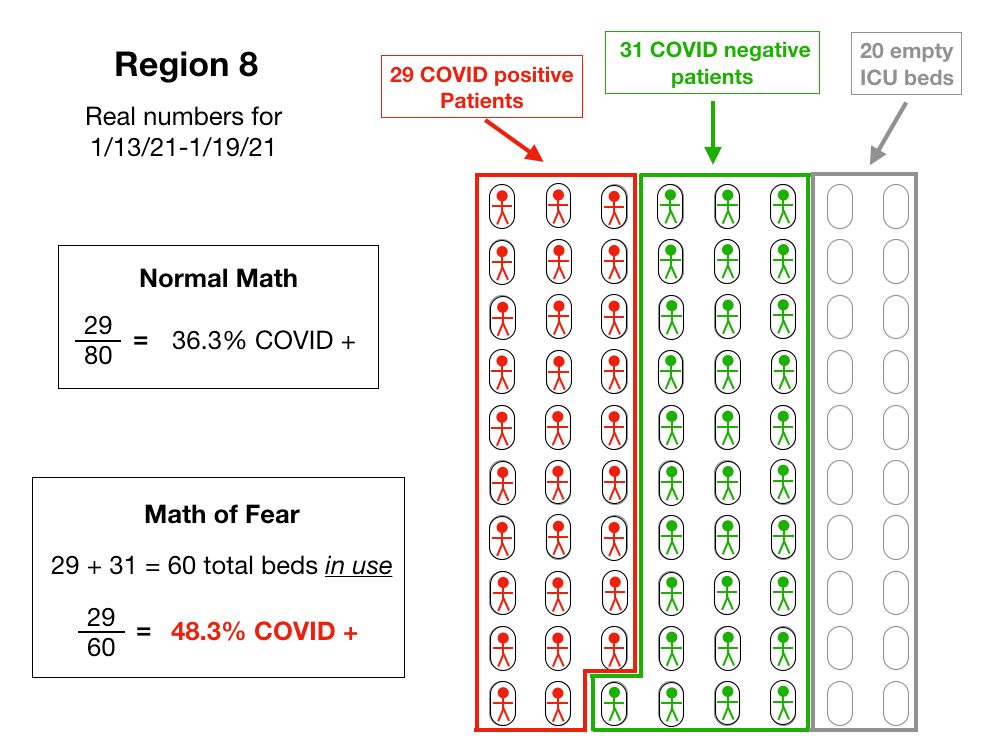
By manipulating the numbers, they have increased the real percentage by a third.
More from Maths
In light of my tweet thread about the category of finite sets and commutative monoids (https://t.co/jnY0wZZbxq), I thought I might try to say what the analogue is for braided monoidal things (although much of this is still somewhat hypothetical).
It's also just kind of a cool combinatorial structure! I've been talking to @CreeepyJoe about this lately, as well as @grassmannian.
The first thing you have to know is that, in a braided monoidal category you can still have commutative monoids. Since a braided monoidal category C has a "twist" map for every object β(x):x⊗x→x⊗x, if x is a monoid you can ask for the following diagram to commute:

Remember that being symmetric monoidal just means that if you take the twist map above and do it twice, you get the identity map, but braided monoidal doesn't mean that. But it's okay! You can still define commutative monoids here.
But so anyway, we can talk about commutative monoids in braided monoidal categories.
So okay, here's a thread on the category of finite sets and a way in which it controls algebraic structure in symmetric monoidal categories. I think it's some really pretty stuff.
— Jonathan Beardsley (@JBeardsleyMath) December 6, 2020
It's also just kind of a cool combinatorial structure! I've been talking to @CreeepyJoe about this lately, as well as @grassmannian.
The first thing you have to know is that, in a braided monoidal category you can still have commutative monoids. Since a braided monoidal category C has a "twist" map for every object β(x):x⊗x→x⊗x, if x is a monoid you can ask for the following diagram to commute:

Remember that being symmetric monoidal just means that if you take the twist map above and do it twice, you get the identity map, but braided monoidal doesn't mean that. But it's okay! You can still define commutative monoids here.
But so anyway, we can talk about commutative monoids in braided monoidal categories.

























