Categories For later read
Let's recap some shenanigans - #Ward45 sure had plenty
In January, Jimmy called out The Crew at Copernicus
A photo bomber, a bounty, and the mayor visited us
https://t.co/YHgWKxWv8m

Stay tuned for the #livetweet of this #45theward community meaning.
— RhymeNoxious (@BlondeNoxious) January 28, 2020
Sarcasm and hyperbole probably unintentional.
Please forgive typos. It's been a long day. pic.twitter.com/ZmhUWv1SNl
The Point is resurrected in February - now ten storeys instead of 10
A firetruck can’t make a turn and Cuyler Plaza meets its end
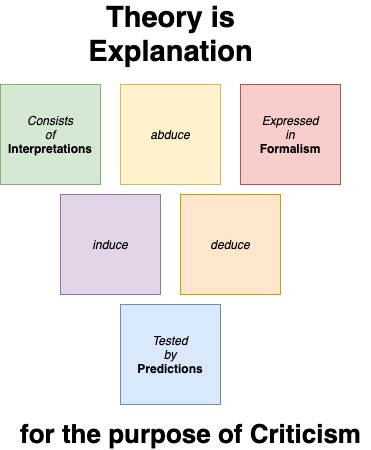
Jimmy shows how tough he is and takes a stand against graffiti
A vigilante video offering a hundred-dollar bounty
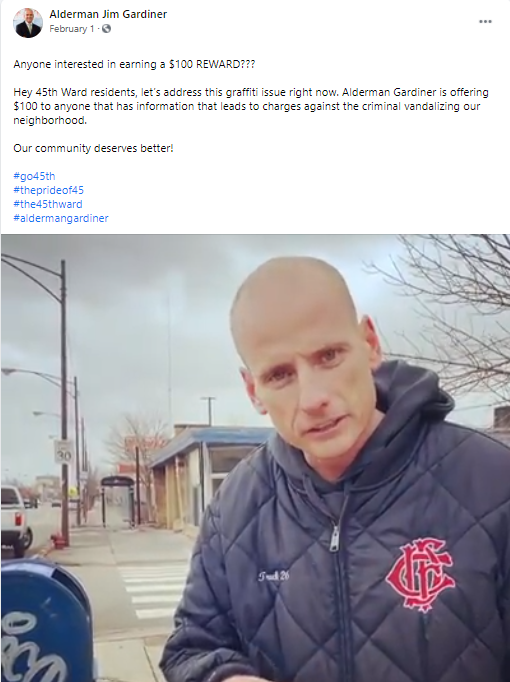
March first Jimmy does the polar plunge with Team Alderbear
And barely wins committeeman - his enormous signs everywhere
In April Willie Wilson donates masks, Jimmy hands out burgers Epically
He can't seem to figure out how to wear a mask properly
In May at the little free library we meet (with complements) Al Chemist
Jimmy patrols the ward from the threat of antifa activitists

It’s June and Jimmy is hiding behind his office
While constituents march for racial justice
“Where’s Jim Gardiner” the crowd chants
Asked if he believes Black lives matter by a Black man
Jim doesn’t answer, instead just deflects
A defining cowardly moment - one we won’t forget
Make better choices, America
This is a fundamentally violent and abusive
The commitment to the ahistoricism of of "this is not who we are" is not merely objectionable. It is actively dangerous.
You can't fix something that you refuse to acknowledge is
Joe has GOT to cut the "this is not who we are" stuff.
— A Shady Dame From Seville (@SorayaMcDonald) January 6, 2021
It's fundamentally ahistorical. The KKK used to openly march down Pennsylvania gotdamn avenue FFS
Frederick Douglass, in 1852:
"To drag a man in fetters into the grand illuminated temple of liberty, and call upon him to join you in joyous anthems, were inhuman mockery and sacrilegious irony. Do you mean, citizens, to mock me...?”
https://t.co/wbbsbfdMny

Please know that your friendly SmithTweeters give heavy side-eye to Smith’s use of phrases like “savage nations” and “naked savages” and so on. They are obviously shocking to the modern ear, and they should be. #WealthOfTweets #SmithTweets
“Well, it’s the 18th century, what do you expect?” just isn't a sufficient explanation. #WealthOfTweets #SmithTweets
The 21stC changed from talking about the First World/Third World to talking about developed/developing nations. That’s a good change and a respectful one. The terms we use for countries will continue to change. See:
Probably the best way to think about Smith’s use of the term “savage nations” is to think of it as its own developmental stage on its way to a better set of terms for talking about the differences among nations. https://t.co/2wr7yACEv5 #WealthOfTweets #SmithTweets
\U0001f91e ONLINE RAFFLE is available from @bodega for the upcoming "UNLV" Nike Dunk Low Retro. Open until 5 PM ET on 2/16.
— Kicks Deals (@KicksDeals) February 15, 2021
\u27a1\ufe0f\u27a1\ufe0f https://t.co/JxJlyPuJVo pic.twitter.com/zenWOCDg4L
like seriously why not make a ton more of them if they're gonna be so sought-after? they land at outlets? so? nike still makes money off that.
the only reason to keep making them so limited is that they KNOW all that matters is the profit on the flip and if they were readily available FEWER people would want them, not more
the whole system is super broken, but it's just gonna go the way it goes, because at this point it all caters to the secondary market. the only reason Nike can sell Jordan 1s for $200 is because the people buying them can flip them for $500
adjusted for inflation, a $65 AJ1 in 1985 is like $160—and modern-day AJ1s are made from cheaper materials in factories staffed by cheaper workers. they don't HAVE to be $200 retail. but the secondary market nuked the whole concept of what sneakers are "worth"
Help! What precisely is "inductive bias"? Some ML researchers are in the opinion that the machine learning category of \u2018inductive biases\u2019 can allow us to build a causal understanding of the world. My Ladder of Causation says: "This is mathematically impossible". Who is right? 1/
— Judea Pearl (@yudapearl) February 14, 2021
I crucial step on the road towards AGI is a richer vocabulary for reasoning about inductive biases.
explores the apparent impedance mismatch between inductive biases and causal reasoning. But isn't the logical thinking required for good causal reasoning also not an inductive bias?
An inductive bias is what C.S. Peirce would call a habit. It is a habit of reasoning. Logical thinking is like a Platonic solid of the many kinds of heuristics that are discovered.
The kind of black and white logic that is found in digital computers is critical to the emergence of today's information economy. This of course is not the same logic that drives the general intelligence that lives in the same economy.
As we see it, there are 3 recent theories that hit on important aspects of the divergence...
1/
New CEPR Discussion Paper - DP15802
— CEPR (@cepr_org) February 14, 2021
Culture, Institutions & the Long Divergence@albertobisin @nyuniversity, Jared Rubin @jaredcrubin @ChapmanU, Avner Seror @SerorAvner @amseaixmars @univamu, Thierry Verdier @PSEinfohttps://t.co/lhs6AJb7jE#CEPR_DE, #CEPR_EH, #CEPR_ITRE pic.twitter.com/FtMzAELljJ
One set of theories focus on the legitimating power of Islam (Rubin, @prof_ahmetkuru, Platteau). This gave religious clerics greater power, which pulled political resources away form those encouraging economic development
But these theories leave some questions unanswered...
2/
Religious legitimacy is only effective if people
care what religious authorities dictate. Given the economic consequences, why do people remain religious, and thereby render religious legitimacy effective? Is religiosity a cause or a consequence of institutional arrangements?
3/
Another set of theories focus on the religious proscriptions of Islam, particular those associated with Islamic law (@timurkuran). These laws were appropriate for the setting they formed but had unforeseeable consequences and failed to change as economic circumstances changed
4/
There are unaddressed questions here, too
Muslim rulers must have understood that Islamic law carried proscriptions that hampered economic development. Why, then, did they continue to use Islamic institutions (like courts) that promoted inefficiencies?
5/
As is the corollary question being tossed about, "How to heal the Nation?".
There is a #systems principle
An excellent piece that raises a key question going forward:
— Bob Geiger (@GeigerNews) January 16, 2021
Should we ever "unify" with the worst among us?
"Unifying with those seeking white supremacy, voter suppression, and government overthrow seems like the very definition of madness."https://t.co/UgmPQfy05F
that is a powerful insight into these, & related, questions.
"You cannot solve a problem at the same level it was created."
If the problem we were solving for were some detail, 'where to place a road; what $ to allocate to this or that project' sort of thing, then the way to
think about the problem, the impasse, is to appeal first to the functions of prior planning, history - meaning what did we do the last time, maybe pragmatics...Eventually, if the organization (whether business, community, or governance) may make a decision and that becomes the
decision. Often, typically, the decision is some sort of amalgam of the various ideas and 'camps' in the room. Rarely, but sometimes, the decision is made out of pure hierarchy..."What the boss says goes, I don't care what you think..." sort of thing. Largely that is old school
and is not the normal way of conflict resolution. Especially in the context of solving a problem.
But a decision is made, and typically people, and the various factions, come together and get to work in the context of the decision. Sometimes called 'teamwork'.