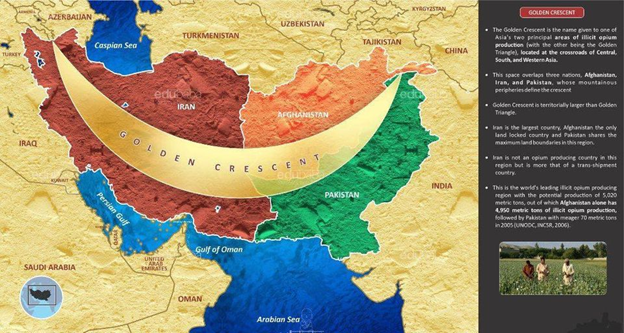
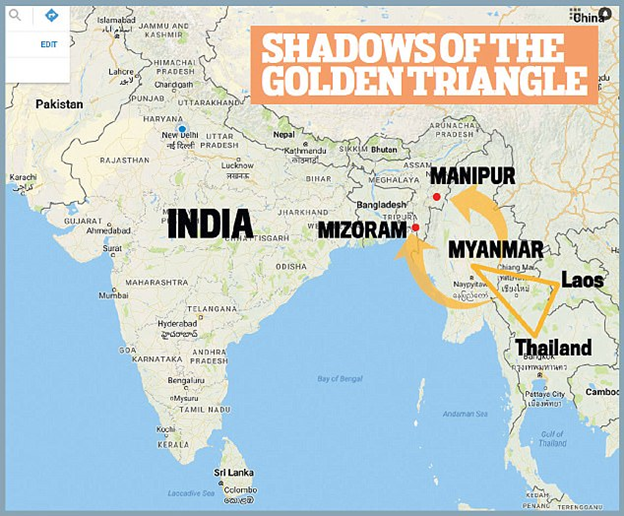
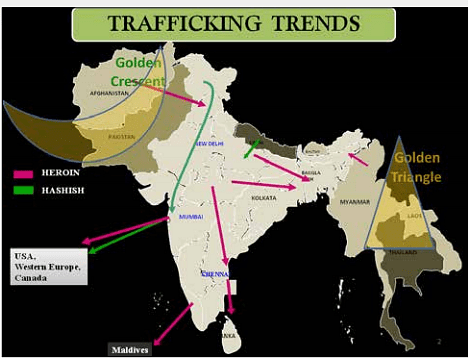
🇬🇧🇪🇺 Who caused Hard Brexit? Some thoughts from the perspective of a social scientist. In the last few days we have seen an interminable debate on whether Remainers, Soft Brexiters, or Hard Brexiters are responsible for Hard Brexit. And it’s a false debate. Why? 1/n
@Sime0nStylites @simonjhix @robfordmancs @anandMenon1 @drjennings @sarahobolt @jillongovt @Dannythefink
More from Brexit
End of week 2 thread on post Brexit food trade
There is continued growing unease. The main picture remains one of depressed/tentative trade (c50% down y-o-y) and some high profile logistics business have taken the rational step to stop and regroup.
The big worry here is that ‘not-trading’becomes a habit. We can’t/won’t carry on at half the volumes of before, but as volumes claw back we may only reach something like 80% of previous volumes and that is a disaster for a food industry already battered by a recession.
Lots of focus has been on the idea of EU businesses stopping serving the UK. Worries about how we feed ourselves has trumped worry about our exporters at every stage. Even though it is the collapse of our export businesses that is (and has always been) the greater threat.
To reassure the mainland British shopper that feels like less of a risk. UK is a large market of wealthy consumers, and UK gov has shown it will do anything (however unfair) to ensure stuff gets in - even letting supermarkets have access to the fast track lane to Dover.
I am not as close to this but it feels like shortage on the shelves is more of a genuine immediate threat for the island of Ireland. The types of innovative solutions we have discussed this week can help but will they come in quick enough?
There is continued growing unease. The main picture remains one of depressed/tentative trade (c50% down y-o-y) and some high profile logistics business have taken the rational step to stop and regroup.
The big worry here is that ‘not-trading’becomes a habit. We can’t/won’t carry on at half the volumes of before, but as volumes claw back we may only reach something like 80% of previous volumes and that is a disaster for a food industry already battered by a recession.
Lots of focus has been on the idea of EU businesses stopping serving the UK. Worries about how we feed ourselves has trumped worry about our exporters at every stage. Even though it is the collapse of our export businesses that is (and has always been) the greater threat.
To reassure the mainland British shopper that feels like less of a risk. UK is a large market of wealthy consumers, and UK gov has shown it will do anything (however unfair) to ensure stuff gets in - even letting supermarkets have access to the fast track lane to Dover.
NEW. \U0001f6a8\U0001f6a8\U0001f69b\U0001f1ec\U0001f1e7\U0001f644\U0001f69b\U0001f69a\U0001f6a8\U0001f6a8 clear signs govt is preparing for coming #brexit turbulence - consulting on new fast-track scheme for food lorries returning to Europe /1
— Peter Foster (@pmdfoster) January 13, 2021
https://t.co/QqDKxBUu3f
I am not as close to this but it feels like shortage on the shelves is more of a genuine immediate threat for the island of Ireland. The types of innovative solutions we have discussed this week can help but will they come in quick enough?
You May Also Like
A brief analysis and comparison of the CSS for Twitter's PWA vs Twitter's legacy desktop website. The difference is dramatic and I'll touch on some reasons why.
Legacy site *downloads* ~630 KB CSS per theme and writing direction.
6,769 rules
9,252 selectors
16.7k declarations
3,370 unique declarations
44 media queries
36 unique colors
50 unique background colors
46 unique font sizes
39 unique z-indices
https://t.co/qyl4Bt1i5x

PWA *incrementally generates* ~30 KB CSS that handles all themes and writing directions.
735 rules
740 selectors
757 declarations
730 unique declarations
0 media queries
11 unique colors
32 unique background colors
15 unique font sizes
7 unique z-indices
https://t.co/w7oNG5KUkJ

The legacy site's CSS is what happens when hundreds of people directly write CSS over many years. Specificity wars, redundancy, a house of cards that can't be fixed. The result is extremely inefficient and error-prone styling that punishes users and developers.
The PWA's CSS is generated on-demand by a JS framework that manages styles and outputs "atomic CSS". The framework can enforce strict constraints and perform optimisations, which is why the CSS is so much smaller and safer. Style conflicts and unbounded CSS growth are avoided.
Legacy site *downloads* ~630 KB CSS per theme and writing direction.
6,769 rules
9,252 selectors
16.7k declarations
3,370 unique declarations
44 media queries
36 unique colors
50 unique background colors
46 unique font sizes
39 unique z-indices
https://t.co/qyl4Bt1i5x

PWA *incrementally generates* ~30 KB CSS that handles all themes and writing directions.
735 rules
740 selectors
757 declarations
730 unique declarations
0 media queries
11 unique colors
32 unique background colors
15 unique font sizes
7 unique z-indices
https://t.co/w7oNG5KUkJ

The legacy site's CSS is what happens when hundreds of people directly write CSS over many years. Specificity wars, redundancy, a house of cards that can't be fixed. The result is extremely inefficient and error-prone styling that punishes users and developers.
The PWA's CSS is generated on-demand by a JS framework that manages styles and outputs "atomic CSS". The framework can enforce strict constraints and perform optimisations, which is why the CSS is so much smaller and safer. Style conflicts and unbounded CSS growth are avoided.