So we had to develop technologies like this to barely manage control over limited areas in Iraq's few urban centers. Only ~8 in 100 Iraqi adults owns a personal vehicle. That rate is > 1 car/adult in America yet I have never seen any doctrine paper or work of fiction address this
Hey guys, just a friendly reminder. We're watching you. pic.twitter.com/bGwi1uJBwT
— CIA Metadata Analyst with 8 kids (@CiaKids) September 23, 2019
More from Tech
I think about this a lot, both in IT and civil infrastructure. It looks so trivial to “fix” from the outside. In fact, it is incredibly draining to do the entirely crushing work of real policy changes internally. It’s harder than drafting a blank page of how the world should be.
I’m at a sort of career crisis point. In my job before, three people could contain the entire complexity of a nation-wide company’s IT infrastructure in their head.
Once you move above that mark, it becomes exponentially, far and away beyond anything I dreamed, more difficult.
And I look at candidates and know-everything’s who think it’s all so easy. Or, people who think we could burn it down with no losses and start over.
God I wish I lived in that world of triviality. In moments, I find myself regretting leaving that place of self-directed autonomy.
For ten years I knew I could build something and see results that same day. Now I’m adjusting to building something in my mind in one day, and it taking a year to do the due-diligence and edge cases and documentation and familiarization and roll-out.
That’s the hard work. It’s not technical. It’s not becoming a rockstar to peers.
These people look at me and just see another self-important idiot in Security who thinks they understand the system others live. Who thinks “bad” designs were made for no reason.
Who wasn’t there.
The tragedy of revolutionaries is they design a utopia by a river but discover the impure city they razed was on stilts for a reason.
— SwiftOnSecurity (@SwiftOnSecurity) June 19, 2016
I’m at a sort of career crisis point. In my job before, three people could contain the entire complexity of a nation-wide company’s IT infrastructure in their head.
Once you move above that mark, it becomes exponentially, far and away beyond anything I dreamed, more difficult.
And I look at candidates and know-everything’s who think it’s all so easy. Or, people who think we could burn it down with no losses and start over.
God I wish I lived in that world of triviality. In moments, I find myself regretting leaving that place of self-directed autonomy.
For ten years I knew I could build something and see results that same day. Now I’m adjusting to building something in my mind in one day, and it taking a year to do the due-diligence and edge cases and documentation and familiarization and roll-out.
That’s the hard work. It’s not technical. It’s not becoming a rockstar to peers.
These people look at me and just see another self-important idiot in Security who thinks they understand the system others live. Who thinks “bad” designs were made for no reason.
Who wasn’t there.
The 12 most important pieces of information and concepts I wish I knew about equity, as a software engineer.
A thread.
1. Equity is something Big Tech and high-growth companies award to software engineers at all levels. The more senior you are, the bigger the ratio can be:

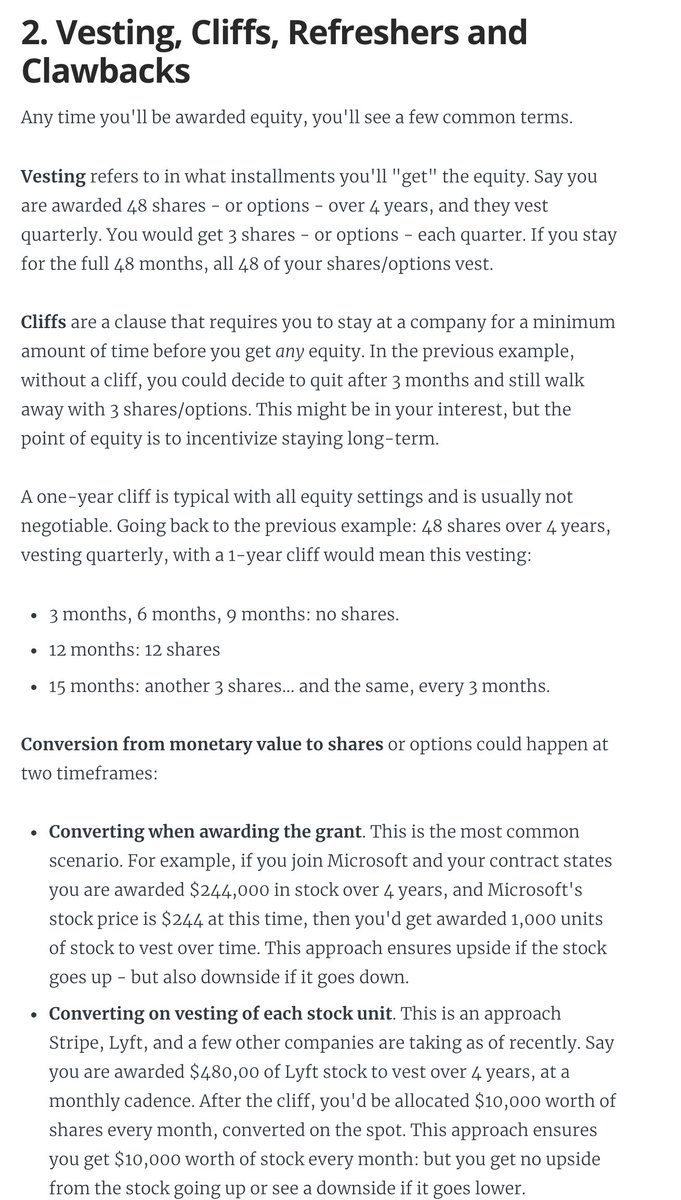
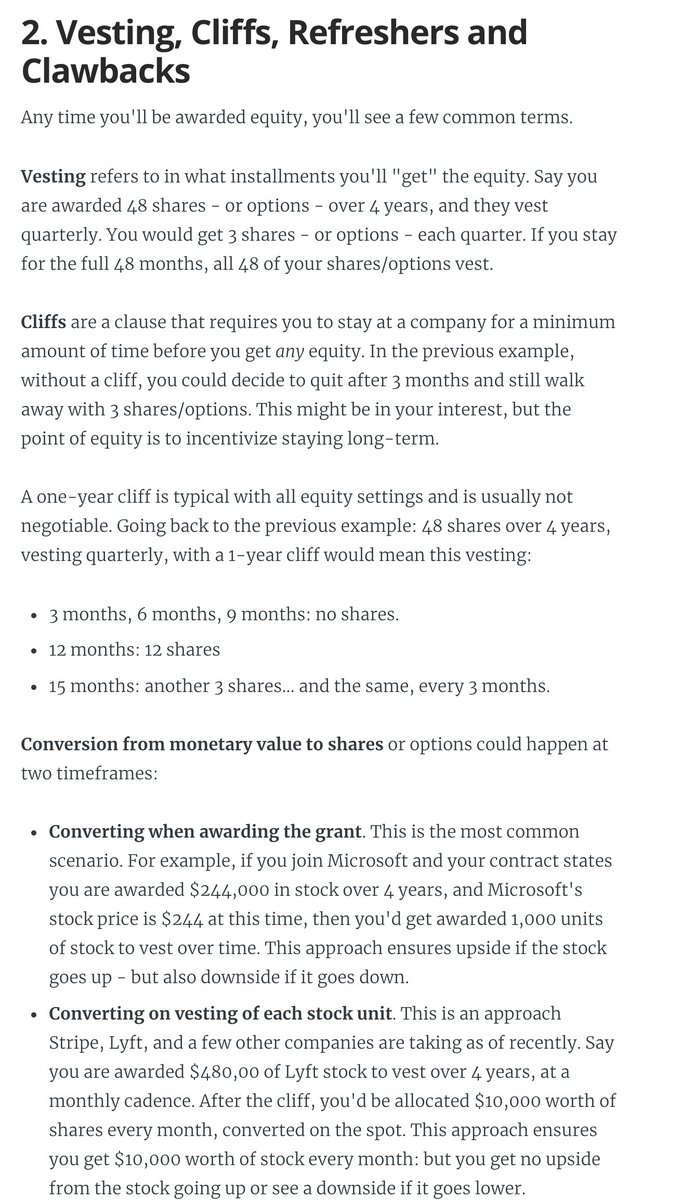
2. Vesting, cliffs, refreshers, and sign-on clawbacks.
If you get awarded equity, you'll want to understand vesting and cliffs. A 1-year cliff is pretty common in most places that award equity.
Read more in this blog post I wrote: https://t.co/WxQ9pQh2mY
3. Stock options / ESOPs.
The most common form of equity compensation at early-stage startups that are high-growth.
And there are *so* many pitfalls you'll want to be aware of. You need to do your research on this: I can't do justice in a tweet.
https://t.co/cudLn3ngqi
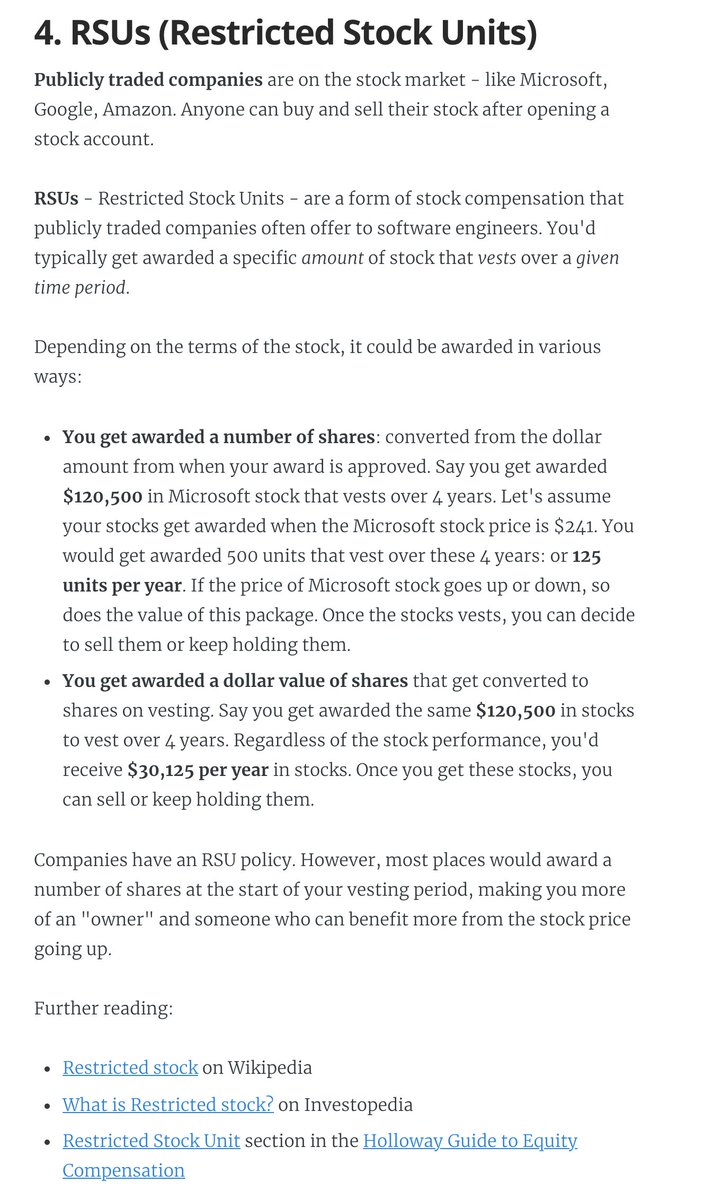
4. RSUs (Restricted Stock Units)
A common form of equity compensation for publicly traded companies and Big Tech. One of the easier types of equity to understand: https://t.co/a5xU1H9IHP
5. Double-trigger RSUs. Typically RSUs for pre-IPO companies. I got these at Uber.
6. ESPP: a (typically) amazing employee perk at publicly traded companies. There's always risk, but this plan can typically offer good upsides.
7. Phantom shares. An interesting setup similar to RSUs... but you don't own stocks. Not frequent, but e.g. Adyen goes with this plan.

A thread.
1. Equity is something Big Tech and high-growth companies award to software engineers at all levels. The more senior you are, the bigger the ratio can be:

2. Vesting, cliffs, refreshers, and sign-on clawbacks.
If you get awarded equity, you'll want to understand vesting and cliffs. A 1-year cliff is pretty common in most places that award equity.
Read more in this blog post I wrote: https://t.co/WxQ9pQh2mY

3. Stock options / ESOPs.
The most common form of equity compensation at early-stage startups that are high-growth.
And there are *so* many pitfalls you'll want to be aware of. You need to do your research on this: I can't do justice in a tweet.
https://t.co/cudLn3ngqi

4. RSUs (Restricted Stock Units)
A common form of equity compensation for publicly traded companies and Big Tech. One of the easier types of equity to understand: https://t.co/a5xU1H9IHP
5. Double-trigger RSUs. Typically RSUs for pre-IPO companies. I got these at Uber.

6. ESPP: a (typically) amazing employee perk at publicly traded companies. There's always risk, but this plan can typically offer good upsides.
7. Phantom shares. An interesting setup similar to RSUs... but you don't own stocks. Not frequent, but e.g. Adyen goes with this plan.
















