This is the exact problem with our government's thinking & response- despite this strategy of 'tolerating deaths' and half-way measures having spectacularly failed, it's quite amazing that our govt still hasn't learned anything, & continues to promote a policy of death. Thread
U.K. needs to confront
— Esther McVey (@EstherMcVey1) January 2, 2021
\u2018The challenge that faces us is to decide - are we going to try to pursue the elimination of Covid-19 regardless of the costs or decide on a tolerable level of deaths (like we do with the flu) in order to return to a normal life?\u2019
https://t.co/9hWbHIPJUq
https://t.co/VPqJBbkFik
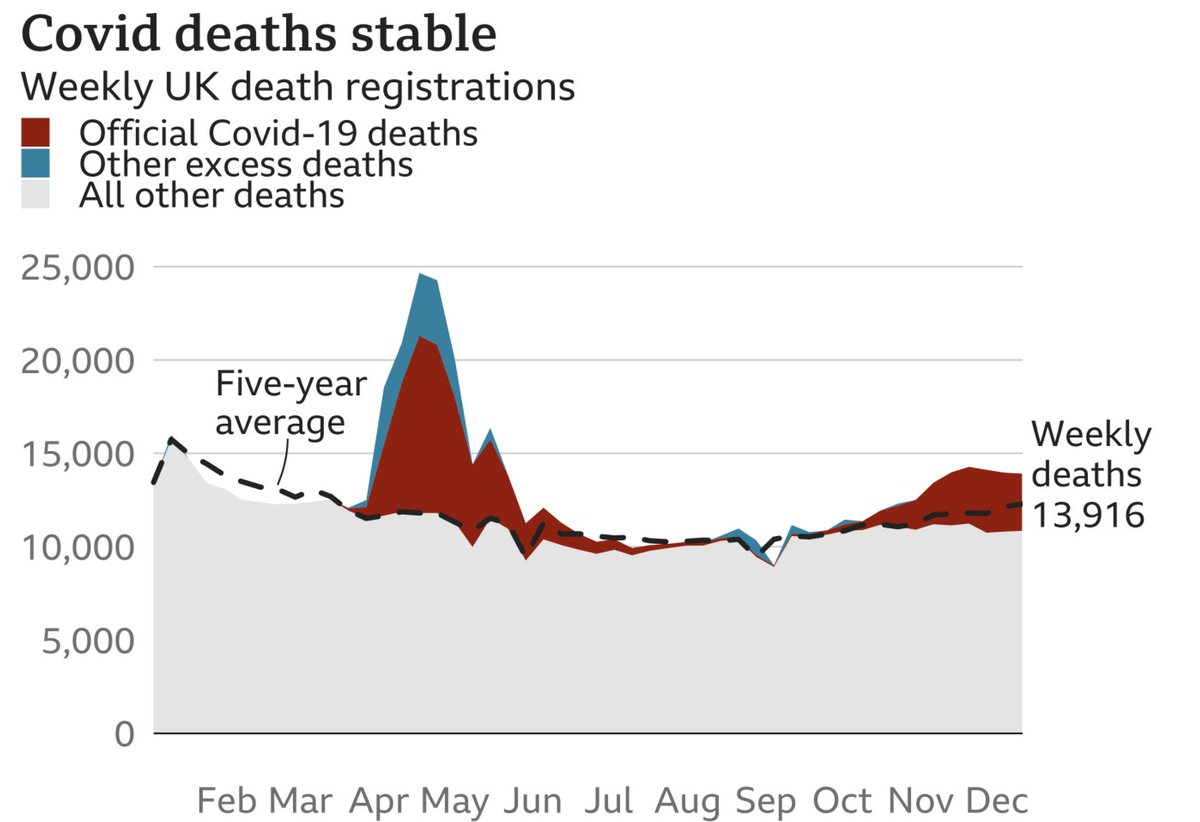
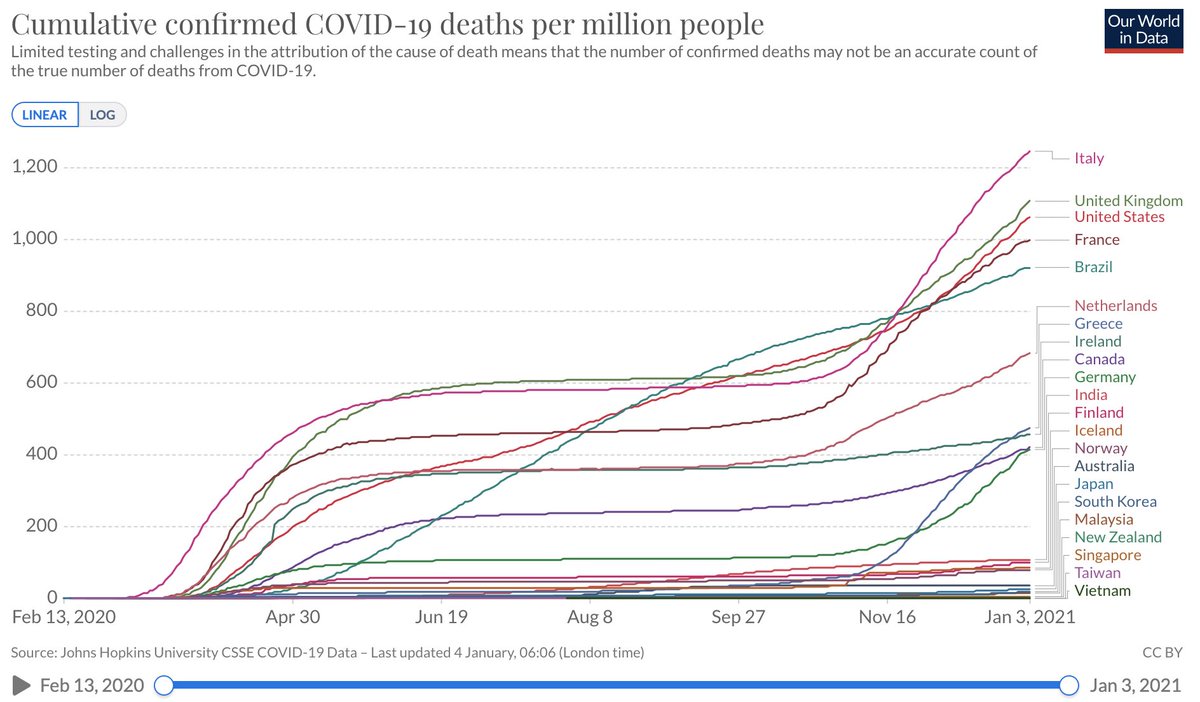
The govt has completely failed us & their continued pursuit of pseudoscience will cost many more lives.
More from Deepti Gurdasani
First, there is strong evidence to support increased transmissibility of B117 - current estimates of increased transmissibility range between 30-70% - from epidemiological evidence examining the differential rate of growth of B117 with respect to other variants & increase in R
There is also evidence from PHE contact studies that the risk of transmission from those carrying the B117 variant is ~50% greater than with other non-B117 variants.
Increased transmissibility, even if a variant has the same fatality rate can increase deaths substantially, because the rate of growth of cases is higher- & more cases means more deaths.
Increased fatality rates also increase deaths- but do so
How dangerous are the B.1.1.7 and 501Y.V2 hyper-transmissible strains?
— Eric Topol (@EricTopol) January 11, 2021
by @AdamJKucharski @CFR_orghttps://t.co/aycWMN3b5h
h/t @Karl_Lauterbach pic.twitter.com/JlaFzzP06t
So how was risk of death with the variant studied?
We don't routinely sequence all samples for the virus. We've found that the variant has a particular deletion which means that some PCR tests on samples with the variant give a different read-out when the variant is present.
Questions have to be asked about the evidence Jenny Harries gave to the Education Committee today about the risk to teachers.
— Adam Hamdy (@adamhamdy) January 19, 2021
Was she aware of this data?
If not, why wasn\u2019t she properly briefed?#COVID19 #schools https://t.co/4wa1PyAJld pic.twitter.com/eqFjaA1zYC
data shows *both* primary & secondary school teachers are at double the risk of confirmed infection relative to comparable positivity in the general population. ONS household infection data also clearly show that children are important sources of transmission.
Yet, in the parliamentary select meeting today, witnesses like Jenny Harries repeated the same claims- that have been debunked by the ONS data, and the data released by the @educationgovuk today. How many lives have been lost to these lies? How many more people have long COVID?
has repeatedly pointed out errors & gaps in the ONS reporting of evidence around risk of infection among teachers- and it's taken *months* to get clarity on this. The released data are a result of months of campaigning by her, the @NEU and others.
Rather than being transparent about the risk of transmission in school settings & mitigating this, the govt (& many of its advisors) has engaged in dismissing & denying evidence that's been clear for a while. Evidence from the govt's own surveys. And global evidence.
Why?
I've heard a lot of scientists claim these three - including most recently the chief advisor to the CDC, where the claim that most transmission doesn't happen within the walls of schools. There is strong evidence to rebut this claim. Let's look at
The science shows us that most disease transmission does not happen in the walls of the school, but it comes in from the community. So, CDC is advocating to get our K-5 students back in school at least in a hybrid mode with universal mask wearing and 6 ft of distancing. https://t.co/dfvJ2nl2s4
— Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH (@CDCDirector) February 14, 2021
Let's look at the trends of infection in different age groups in England first- as reported by the ONS. Being a random survey of infection in the community, this doesn't suffer from the biases of symptom-based testing, particularly important in children who are often asymptomatic
A few things to note:
1. The infection rates among primary & secondary school children closely follow school openings, closures & levels of attendance. E.g. We see a dip in infections following Oct half-term, followed by a rise after school reopening.
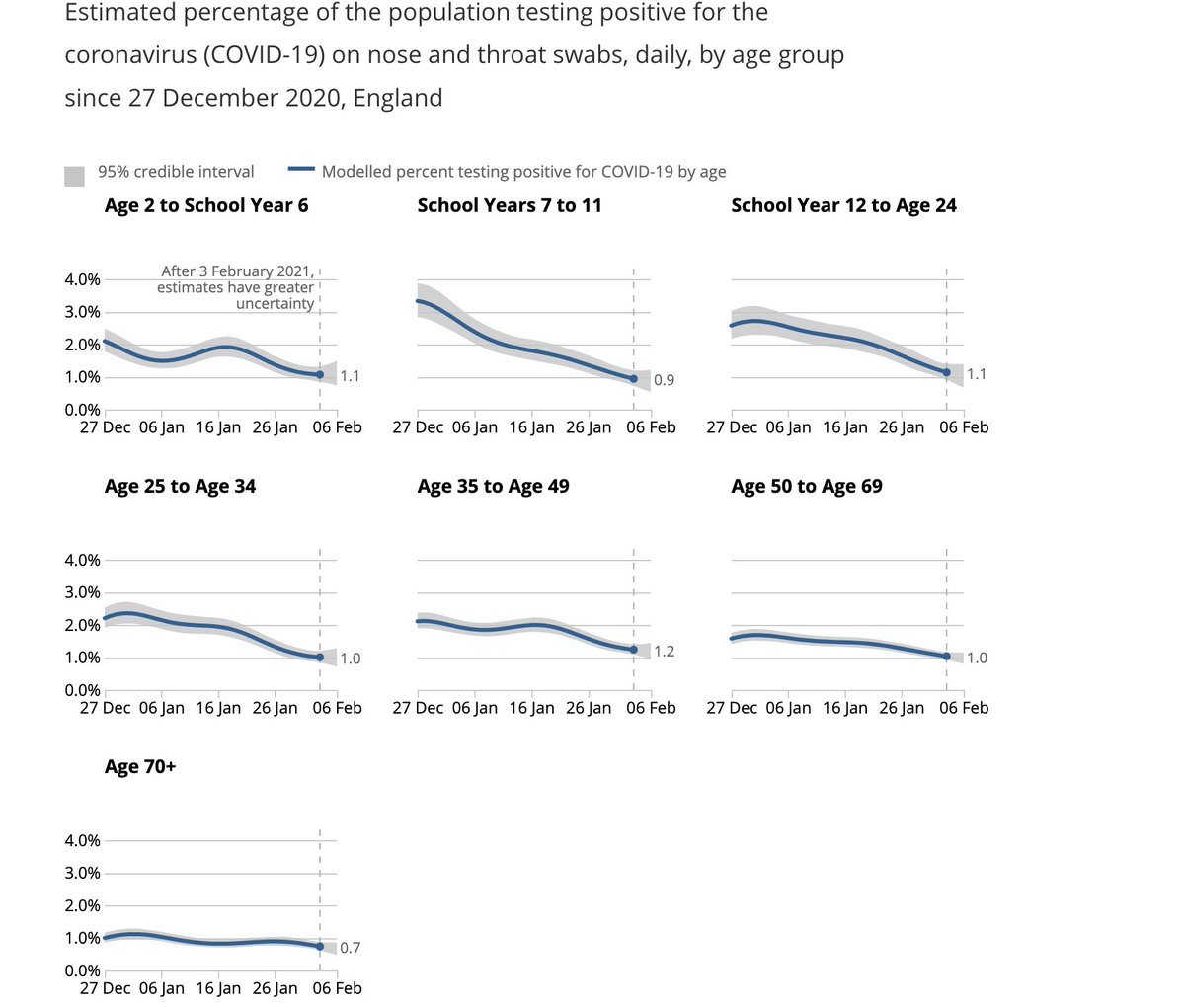
We see steep drops in both primary & secondary school groups after end of term (18th December), but these drops plateau out in primary school children, where attendance has been >20% after re-opening in January (by contrast with 2ndary schools where this is ~5%).
More from Government
{“Shots fired across the bow”}
{Warning to traitors}
{Light will reveal the evil plans}
{You were warned traitors}
As background to tweets I am about to post, you should read this article carefully. I ask that you read each of my tweets carefully & decide if the information conveyed demands that Patriots rise up so that every lie will be revealed.@realDonaldTrumphttps://t.co/9KIX4DEtha
— Lin Wood (@LLinWood) January 4, 2021
You May Also Like
Flat Earth conference attendees explain how they have been brainwashed by YouTube and Infowarshttps://t.co/gqZwGXPOoc
— Raw Story (@RawStory) November 18, 2018
This spring at SxSW, @SusanWojcicki promised "Wikipedia snippets" on debated videos. But they didn't put them on flat earth videos, and instead @YouTube is promoting merchandising such as "NASA lies - Never Trust a Snake". 2/

A few example of flat earth videos that were promoted by YouTube #today:
https://t.co/TumQiX2tlj 3/
https://t.co/uAORIJ5BYX 4/
https://t.co/yOGZ0pLfHG 5/
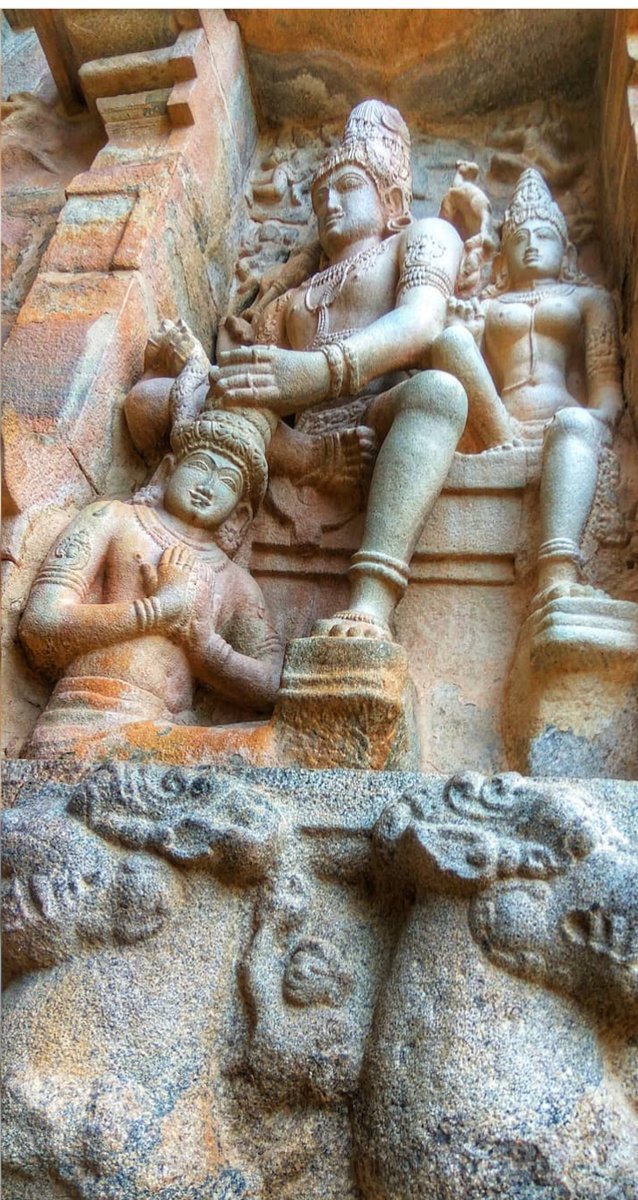
Chandesha-Anugraha Murti - One of the Sculpture in Brihadeshwara Temple at Gangaikonda Cholapuram - built by Raja Rajendra Chola I
This Sculpture depicts Bhagwan Shiva along with Devi Paravathi blessing Chandeshwara - one of the 63 Nayanmars.
#Thread

Chandeshwara/Chandikeshwara is regarded as custodian of Shiva Temple's wealth&most of Shiva temples in South India has separate sannathi for him.
His bhakti for Bhagwan Shiva elevated him as one of foremost among Nayanmars.
He gave importance to Shiva Pooja&protection of cows.

There are series of paintings, illustrating the #story of Chandikeshwar in the premises of
Sri Sathiyagireeswarar #Temple at Seinganur,near Kumbakonam,TN
Chandikeshwara's birth name
is Vichara sarman.He was born in the village of Senganur on the banks of River Manni.

His Parent names were Yajnathatan and Pavithrai.
Vichara Sarman was a gifted child and he learnt Vedas and Agamas at a very young age.
He was very devout and would always think about Bhagwan Shiva.
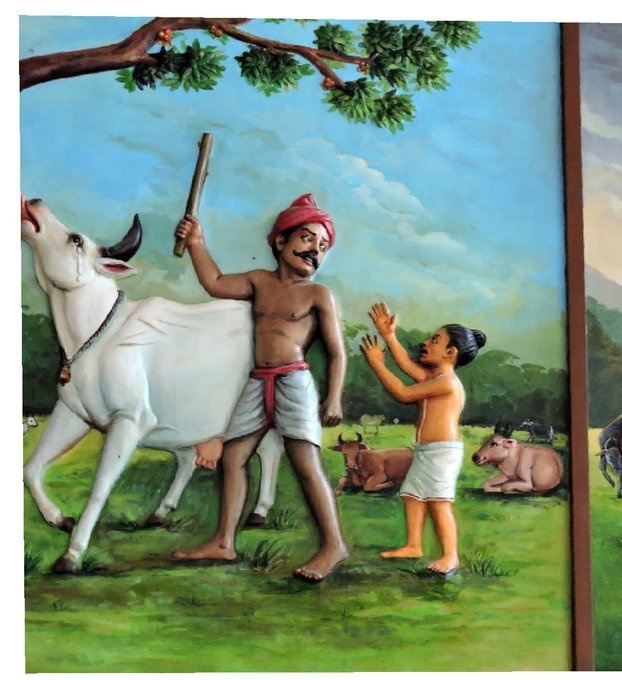
One day he saw a cowherd man brutally assaulting a cow,Vichara Sarman could not tolerate this. He spoke to cowherd: ‘Do you not know that the cow is worshipful & divine? All gods & Devas reside in https://t.co/ElLcI5ppsK it is our duty to protect cows &we should not to harm them.





















