“Selling your winners and holding your losers is like cutting the flowers and watering the weeds.”
Peter Lynch averaged 29.2% annual return between 1977 to 1990.
His books One Up Wall Street and Beating the Street offered great insights into his success.
Here are my top 10 lessons from the legend:

“Selling your winners and holding your losers is like cutting the flowers and watering the weeds.”
“People who succeed in the stock market also accept periodic losses, setbacks, and unexpected occurrences. Calamitous drops do not scare them out of the game.”
"Owning stocks is like having children. Don't get involved with more than you can handle."
"There's no shame in losing money on a stock. Everybody does it. What is shameful is to hold on to a stock, or worse, to buy more of it when the fundamentals are deteriorating."
“This is one of the keys to successful investing: focus on the companies, not on the stocks.”
"While catching up on the news is merely depressing to the citizen who has no stocks, it is a dangerous habit for the investor."
"Never invest in any company before you've done the homework on the company's earnings, prospects, financial condition, competitive position, plans for expansion, and so forth."
"The stock market demands conviction as surely as it victimizes the unconvinced."
"In stocks – as in romance – ease of divorce is not a sound basis for commitment."
"If you can't find any companies that you think are attractive, put your money in the bank until you discover some."
• Investing.
• Business breakdowns.
• Company updates.
Every week.
https://t.co/96pjE7aGBm
More from Thomas Chua
Rather, I learned 10x more about investing from Twitter University.
🧵 Here are 5 threads from world-class Fintwitters.
What you learn: Build an investing checklist.
From: @BrianFeroldi, writer at Motley
1/ How to create an investment checklist (thread)
— Brian Feroldi (@BrianFeroldi) December 8, 2020
Checklists are an amazing, FREE, underutilized investing tool
Here's the step-by-step process for how to create your own
\u2b07\ufe0f\u2b07\ufe0f\u2b07\ufe0f\u2b07\ufe0f\u2b07\ufe0f\u2b07\ufe0f\u2b07\ufe0f\u2b07\ufe0f\u2b07\ufe0f
What you learn: Read 10Ks like a Hedge Fund
From: @FabiusMercurius
\U0001f9d0How to Read 10Ks Like a Hedge Fund\U0001f9d0
— Ming Zhao (@FabiusMercurius) May 7, 2021
\u201cFundamentals don\u2019t matter anymore!\u201d I\u2019ve heard this a lot lately on Fintwit.\U0001f644
But, for those who\u2019ve diversify beyond $GME and $DOGE, here\u2019s a primer on what metrics fundamental buy-side PMs look at and why:
(real examples outlined)
\U0001f447 pic.twitter.com/tLlNRvpnDK
What you learn: Perform a DCF analysis.
From: @10kdiver
1/
— 10-K Diver (@10kdiver) August 8, 2020
Get a cup of coffee.
In this thread, I'll show you how to do a DCF analysis.
For those unfamiliar, DCF = Discounted Cash Flow.
What you learn: When to sell your stocks
From: @borrowed_ideas, founder at
Even after investing for 14 years, I uncover new insights every time I reread his letters.
Recently, I reread his letters from 1977 to 2020 for a third time.
Here are my key insights:

1. Moat is NEVER stagnant
A company's competitive position either grows stronger or weaker each day.
Widening the moat must always take precedence over short-term targets.

2. Commodity businesses
A business without moat will have its returns competed away.
Regardless of improvement, your competitors will quickly copy your advantage away.
Where returns on capital is dismal, reinvestment will only destroy value.

3. The flywheel effect
Buffett was preaching about the flywheel effect before it became cool.
Back then, newspapers were similar to today's platform businesses like Amazon, Meta, and App Store.
More readers beget more advertisers beget more readers.

4. Operating leverage
Companies with high fixed costs and low variable costs will see earnings rise faster than revenue.
However, it cuts both ways.
It becomes a disaster when revenue is declining.
Check out my article on how operating leverage works: https://t.co/Nv747oBAK0

More from Books
You May Also Like
Chandesha-Anugraha Murti - One of the Sculpture in Brihadeshwara Temple at Gangaikonda Cholapuram - built by Raja Rajendra Chola I
This Sculpture depicts Bhagwan Shiva along with Devi Paravathi blessing Chandeshwara - one of the 63 Nayanmars.
#Thread
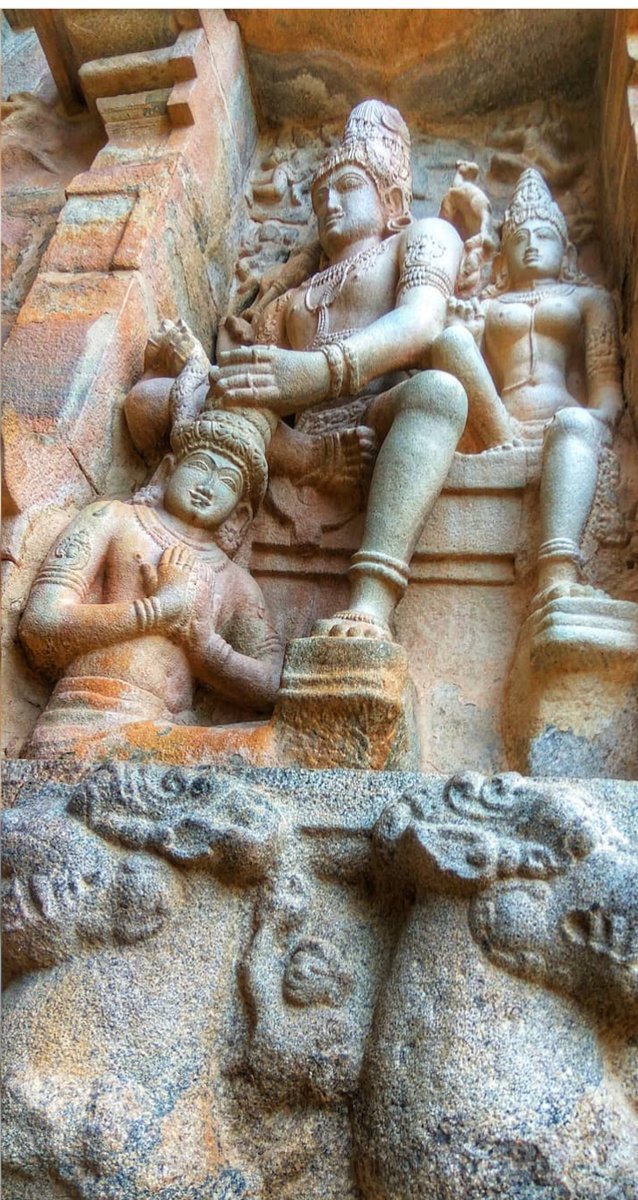

Chandeshwara/Chandikeshwara is regarded as custodian of Shiva Temple's wealth&most of Shiva temples in South India has separate sannathi for him.
His bhakti for Bhagwan Shiva elevated him as one of foremost among Nayanmars.
He gave importance to Shiva Pooja&protection of cows.

There are series of paintings, illustrating the #story of Chandikeshwar in the premises of
Sri Sathiyagireeswarar #Temple at Seinganur,near Kumbakonam,TN
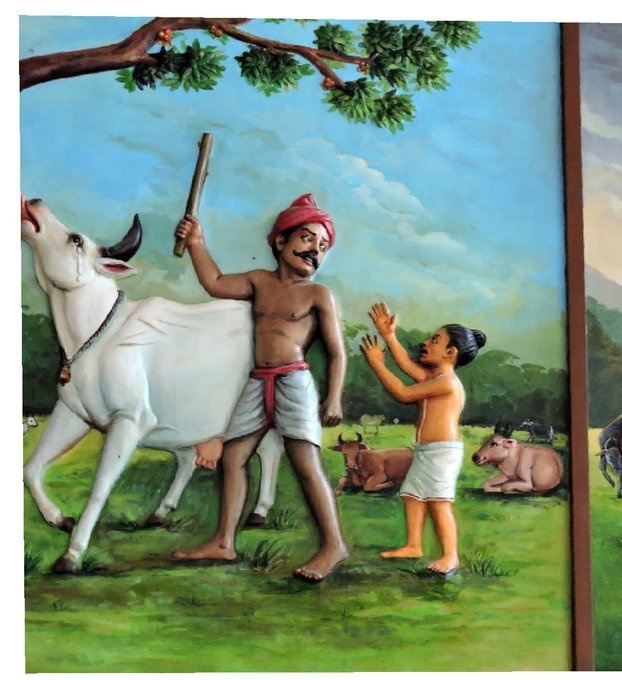
Chandikeshwara's birth name
is Vichara sarman.He was born in the village of Senganur on the banks of River Manni.

His Parent names were Yajnathatan and Pavithrai.
Vichara Sarman was a gifted child and he learnt Vedas and Agamas at a very young age.
He was very devout and would always think about Bhagwan Shiva.
One day he saw a cowherd man brutally assaulting a cow,Vichara Sarman could not tolerate this. He spoke to cowherd: ‘Do you not know that the cow is worshipful & divine? All gods & Devas reside in https://t.co/ElLcI5ppsK it is our duty to protect cows &we should not to harm them.

As a dean of a major academic institution, I could not have said this. But I will now. Requiring such statements in applications for appointments and promotions is an affront to academic freedom, and diminishes the true value of diversity, equity of inclusion by trivializing it. https://t.co/NfcI5VLODi
— Jeffrey Flier (@jflier) November 10, 2018
We know that elite institutions like the one Flier was in (partial) charge of rely on irrelevant status markers like private school education, whiteness, legacy, and ability to charm an old white guy at an interview.
Harvard's discriminatory policies are becoming increasingly well known, across the political spectrum (see, e.g., the recent lawsuit on discrimination against East Asian applications.)
It's refreshing to hear a senior administrator admits to personally opposing policies that attempt to remedy these basic flaws. These are flaws that harm his institution's ability to do cutting-edge research and to serve the public.
Harvard is being eclipsed by institutions that have different ideas about how to run a 21st Century institution. Stanford, for one; the UC system; the "public Ivys".