https://t.co/tkAMShno4k 2/
I've just read one of the most lucid, wide-ranging, cross-disciplinary critiques of cryptocurrency and blockchain I've yet to encounter. 1/

https://t.co/tkAMShno4k 2/
The presence of "externalities" in Rosenthal's title is key. 4/
This is an important critique of libertarianism. 5/
https://t.co/kbmvG5MRbq 11/
https://t.co/bIwXOkJfZH
That democracy itself is incompatible with liberty, since it lets workers vote to limi their bosses:
https://t.co/oL2cBCYJMB 12/
This expense, in turn, compensates miners for the money they pour into defeating Sybil attacks. 21/
This profound wastefulness is a feature, not a bug. 25/
https://t.co/fO5fciIW3u 29/
https://t.co/xbJRf73SZy 35/
https://t.co/jdtbWjOe3C 49/
I. Permissioned blockchains can stop Sybil attacks without cryptocurrency and have no significant externalities; 50/
III. To be successful, permissionless blockchains require proof-of-work or some other deliberately wasteful system, making externalities inevitable; 51/
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Headquarters (modified)
https://t.co/bq5JJPcDcp
CC BY 2.0:
https://t.co/B930sKCLnf 56/
https://t.co/5rhyfeEW7L
More from Cory Doctorow RIGHT-CLICKING WORDCEL MENTALITY
Today's Twitter threads (a Twitter thread).
Inside: Planet Money on HP's myriad ripoffs; Strength in numbers; and more!
Archived at: https://t.co/esjoT3u5Gr
#Pluralistic
1/

On Feb 22, I'm delivering a keynote address for the NISO Plus conference, "The day of the comet: what trustbusting means for digital manipulation."
https://t.co/Z84xicXhGg
2/

Planet Money on HP's myriad ripoffs: Ink-stained wretches of the world, unite!
https://t.co/k5ASdVUrC2
3/
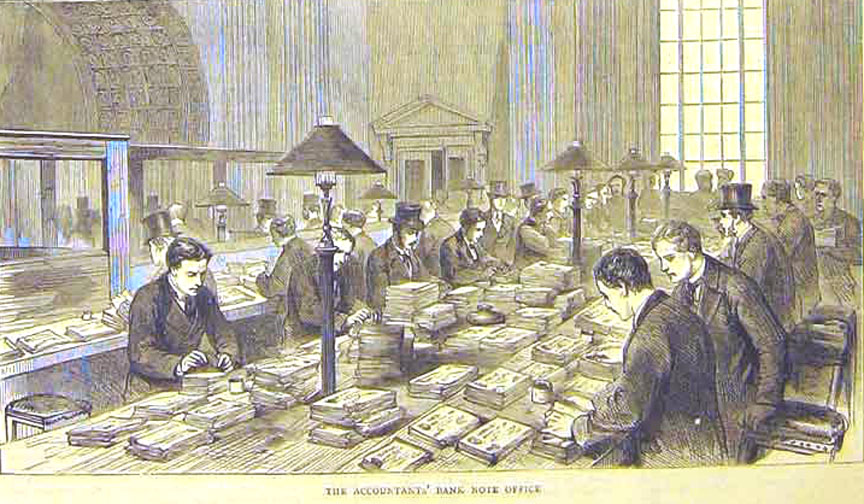
Strength in numbers: The crisis in accounting.
https://t.co/DjfAfHWpNN
4/

#15yrsago Bad Samaritan family won’t return found expensive camera https://t.co/Rn9E5R1gtV
#10yrsago What does Libyan revolution mean for https://t.co/Jz28qHVhrV? https://t.co/dN1e4MxU4r
5/

Inside: Planet Money on HP's myriad ripoffs; Strength in numbers; and more!
Archived at: https://t.co/esjoT3u5Gr
#Pluralistic
1/

On Feb 22, I'm delivering a keynote address for the NISO Plus conference, "The day of the comet: what trustbusting means for digital manipulation."
https://t.co/Z84xicXhGg
2/

Planet Money on HP's myriad ripoffs: Ink-stained wretches of the world, unite!
https://t.co/k5ASdVUrC2
3/

Back in November, I published an article for @EFF about @HP's latest printer-ink ripoff: after offering its customers a free-ink-for-life plan, it unilaterally switched them all to a $1/month-for-life plan.https://t.co/bsc73xPSuo
— Cory Doctorow #BLM (@doctorow) February 18, 2021
1/ pic.twitter.com/tagduPupA5
Strength in numbers: The crisis in accounting.
https://t.co/DjfAfHWpNN
4/

Accountancy is more likely to be mocked than celebrated (or condemned), but accountants, far more than poets, are the unacknowledged legislators of the world.
— Cory Doctorow #BLM (@doctorow) February 18, 2021
1/ pic.twitter.com/FaNQc66gQN
#15yrsago Bad Samaritan family won’t return found expensive camera https://t.co/Rn9E5R1gtV
#10yrsago What does Libyan revolution mean for https://t.co/Jz28qHVhrV? https://t.co/dN1e4MxU4r
5/

More from Crypto
I'm sure someone else has explained this, but it is just so cool and I want to explain how this works.
So Curve is awesome for swaps between similar assets, right? The fact that they trade very close to each other is a key part about how Curve works, using it's custom swap invariant function.
That's step 1
Step 2 is that Synthetix is awesome for creating "synthetic assets" (aka synths) which are assets that trade like other assets, that are backed by another, entirely different asset. Basically, a plastic banana that I can buy and sell like a real banana.
Synthetix has a feature that lets you swap between any two synths with zero slippage and a flat fee. That's because it is simply converting the sythentic asset into another synthetic asset, the backing for the synth doesn't change it just uses a different price oracle now.
This is important. Absolutely no slippage, at any size
Swap $1m sUSD for $1m sBTC? flat 0.3% fee
Swap $10m sUSD for $10m sBTC? flat 0.3% fee
swap $100m sUSD for $100m sBTC? Well, there isn't that many synths in Curve, yet but you get the point. The only limit is the pool depth
— Andre Cronje (@AndreCronjeTech) January 15, 2021
So Curve is awesome for swaps between similar assets, right? The fact that they trade very close to each other is a key part about how Curve works, using it's custom swap invariant function.
That's step 1
Step 2 is that Synthetix is awesome for creating "synthetic assets" (aka synths) which are assets that trade like other assets, that are backed by another, entirely different asset. Basically, a plastic banana that I can buy and sell like a real banana.
Synthetix has a feature that lets you swap between any two synths with zero slippage and a flat fee. That's because it is simply converting the sythentic asset into another synthetic asset, the backing for the synth doesn't change it just uses a different price oracle now.
This is important. Absolutely no slippage, at any size
Swap $1m sUSD for $1m sBTC? flat 0.3% fee
Swap $10m sUSD for $10m sBTC? flat 0.3% fee
swap $100m sUSD for $100m sBTC? Well, there isn't that many synths in Curve, yet but you get the point. The only limit is the pool depth
We are actively working to launch on @binance Smart Chain #BSC .
To make this transition easy & understandable for everyone, we are answering most frequently asked questions here.
Ready? Go! 🔥
1/24
#DeFi #YieldFarming

Q1 - What are the benefits of holding the $VALUE token on the Ethereum Mainnet network? Give me reasons not to sell. Some are assuming that the VALUE token will be abandoned now that vBSWAP is being created. Can you clarify the use case for VALUE?
👉 $VALUE will always be a governance & profit receiving token of the whole ecosystem if staked in #vGov. With the new farming token on #BSC , gvVALUE holders will get extra rewards at BSC if they choose to bridge their gvVALUE to BSC & stake in gvVALUE-B/BUSD 98/2 pool.
Q2 - What do I need to do with my VALUE tokens that are staked in vGov? Is it OK to leave them in the vGov?
👉If you have VALUE but aren't staking in the vGov & you would like to participate in the BSC expansion, you will need to stake your VALUE in the vGov to receive gvVALUE.
If you are staking in vGov but don't see the correct gvVALUE amount in your wallet, go to vGov (https://t.co/udXn5IJtVx) to unlock your gvVALUE from the old contract. There will be a bridge from ETH to BSC to move gvVALUE and vUSD over.
To make this transition easy & understandable for everyone, we are answering most frequently asked questions here.
Ready? Go! 🔥
1/24
#DeFi #YieldFarming

Q1 - What are the benefits of holding the $VALUE token on the Ethereum Mainnet network? Give me reasons not to sell. Some are assuming that the VALUE token will be abandoned now that vBSWAP is being created. Can you clarify the use case for VALUE?
👉 $VALUE will always be a governance & profit receiving token of the whole ecosystem if staked in #vGov. With the new farming token on #BSC , gvVALUE holders will get extra rewards at BSC if they choose to bridge their gvVALUE to BSC & stake in gvVALUE-B/BUSD 98/2 pool.
Q2 - What do I need to do with my VALUE tokens that are staked in vGov? Is it OK to leave them in the vGov?
👉If you have VALUE but aren't staking in the vGov & you would like to participate in the BSC expansion, you will need to stake your VALUE in the vGov to receive gvVALUE.
If you are staking in vGov but don't see the correct gvVALUE amount in your wallet, go to vGov (https://t.co/udXn5IJtVx) to unlock your gvVALUE from the old contract. There will be a bridge from ETH to BSC to move gvVALUE and vUSD over.



























