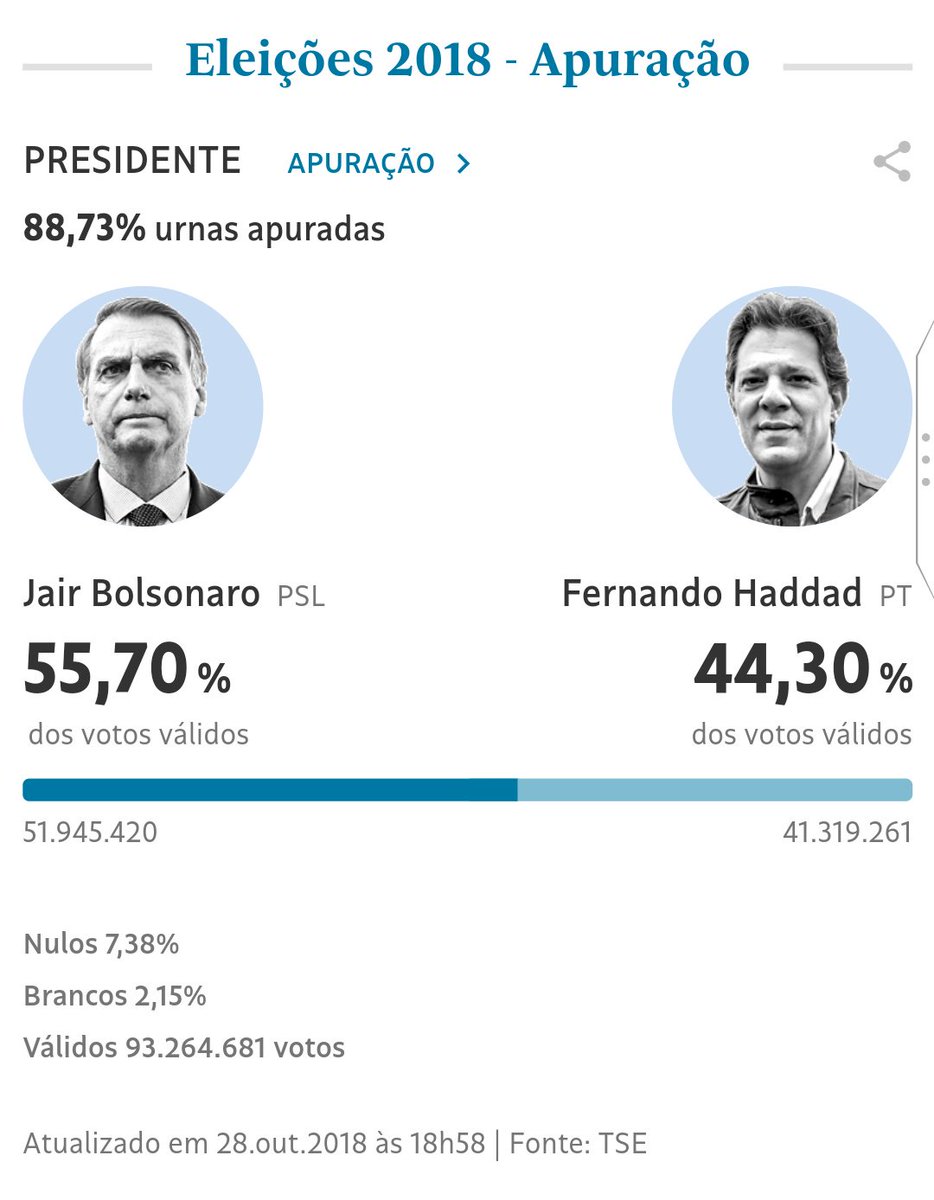
89% of the real results are in (not exit polls) -
55.7% Bolsonaro
44.3% Haddad
Jair Bolsonaro will almost certainly be the next President of Brazil. This is a sad day for fans of democracy and human rights all around the world.

More from All
How can we use language supervision to learn better visual representations for robotics?
Introducing Voltron: Language-Driven Representation Learning for Robotics!
Paper: https://t.co/gIsRPtSjKz
Models: https://t.co/NOB3cpATYG
Evaluation: https://t.co/aOzQu95J8z
🧵👇(1 / 12)
Videos of humans performing everyday tasks (Something-Something-v2, Ego4D) offer a rich and diverse resource for learning representations for robotic manipulation.
Yet, an underused part of these datasets are the rich, natural language annotations accompanying each video. (2/12)
The Voltron framework offers a simple way to use language supervision to shape representation learning, building off of prior work in representations for robotics like MVP (https://t.co/Pb0mk9hb4i) and R3M (https://t.co/o2Fkc3fP0e).
The secret is *balance* (3/12)
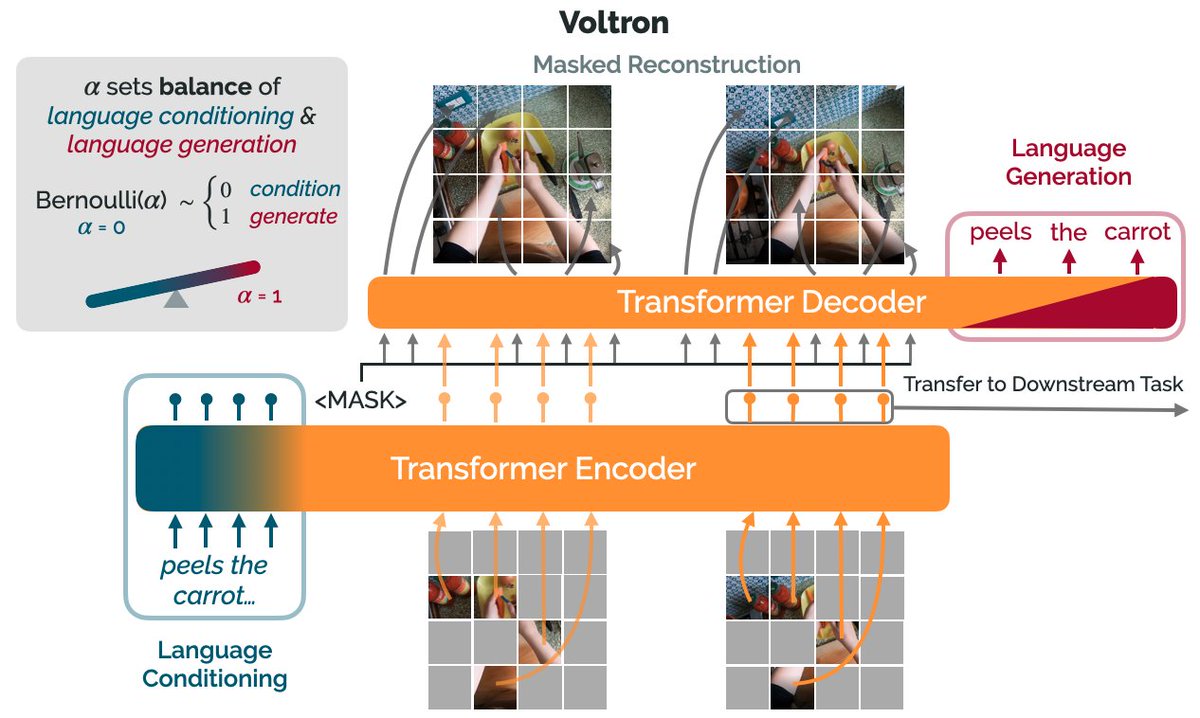
Starting with a masked autoencoder over frames from these video clips, make a choice:
1) Condition on language and improve our ability to reconstruct the scene.
2) Generate language given the visual representation and improve our ability to describe what's happening. (4/12)
By trading off *conditioning* and *generation* we show that we can learn 1) better representations than prior methods, and 2) explicitly shape the balance of low and high-level features captured.
Why is the ability to shape this balance important? (5/12)
Introducing Voltron: Language-Driven Representation Learning for Robotics!
Paper: https://t.co/gIsRPtSjKz
Models: https://t.co/NOB3cpATYG
Evaluation: https://t.co/aOzQu95J8z
🧵👇(1 / 12)

Videos of humans performing everyday tasks (Something-Something-v2, Ego4D) offer a rich and diverse resource for learning representations for robotic manipulation.
Yet, an underused part of these datasets are the rich, natural language annotations accompanying each video. (2/12)
The Voltron framework offers a simple way to use language supervision to shape representation learning, building off of prior work in representations for robotics like MVP (https://t.co/Pb0mk9hb4i) and R3M (https://t.co/o2Fkc3fP0e).
The secret is *balance* (3/12)
Starting with a masked autoencoder over frames from these video clips, make a choice:
1) Condition on language and improve our ability to reconstruct the scene.
2) Generate language given the visual representation and improve our ability to describe what's happening. (4/12)
By trading off *conditioning* and *generation* we show that we can learn 1) better representations than prior methods, and 2) explicitly shape the balance of low and high-level features captured.
Why is the ability to shape this balance important? (5/12)
You May Also Like
First thread of the year because I have time during MCO. As requested, a thread on the gods and spirits of Malay folk religion. Some are indigenous, some are of Indian origin, some have Islamic
Before I begin, it might be worth explaining the Malay conception of the spirit world. At its deepest level, Malay religious belief is animist. All living beings and even certain objects are said to have a soul. Natural phenomena are either controlled by or personified as spirits
Although these beings had to be respected, not all of them were powerful enough to be considered gods. Offerings would be made to the spirits that had greater influence on human life. Spells and incantations would invoke their
Two known examples of such elemental spirits that had god-like status are Raja Angin (king of the wind) and Mambang Tali Arus (spirit of river currents). There were undoubtedly many more which have been lost to time
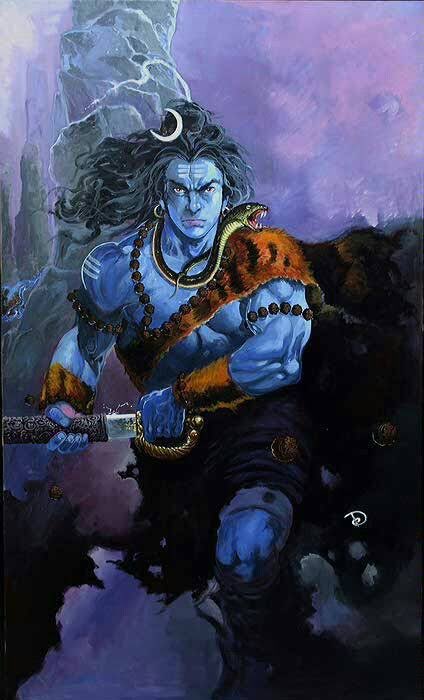
Contact with ancient India brought the influence of Hinduism and Buddhism to SEA. What we now call Hinduism similarly developed in India out of native animism and the more formal Vedic tradition. This can be seen in the multitude of sacred animals and location-specific Hindu gods
i wonder if you can make a thread bout witchcraft in malaysia.. or list of our own local gods/deites..
— r a y a \U0001f319 (@lcvelylilith) February 20, 2020
Before I begin, it might be worth explaining the Malay conception of the spirit world. At its deepest level, Malay religious belief is animist. All living beings and even certain objects are said to have a soul. Natural phenomena are either controlled by or personified as spirits
Although these beings had to be respected, not all of them were powerful enough to be considered gods. Offerings would be made to the spirits that had greater influence on human life. Spells and incantations would invoke their
Animist ceremonies of a religious or magical nature were normally held for the purpose of divination or making a request. This would either be done at a keramat or at a shrine similar to the Thai spirit houses or Chinese roadside shrines pic.twitter.com/I1hliyi0x3
— \u2745\u1710\u170b\u1713\u170e (@uglyluhan) June 16, 2019
Two known examples of such elemental spirits that had god-like status are Raja Angin (king of the wind) and Mambang Tali Arus (spirit of river currents). There were undoubtedly many more which have been lost to time
Contact with ancient India brought the influence of Hinduism and Buddhism to SEA. What we now call Hinduism similarly developed in India out of native animism and the more formal Vedic tradition. This can be seen in the multitude of sacred animals and location-specific Hindu gods